Rapamycin Modulates Glucocorticoid Receptor Function, Blocks Atrophogene REDD1, and Protects Skin from Steroid Atrophy
- PMID: 29596905
- PMCID: PMC6634309
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.02.045
Rapamycin Modulates Glucocorticoid Receptor Function, Blocks Atrophogene REDD1, and Protects Skin from Steroid Atrophy
Abstract
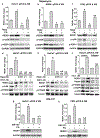
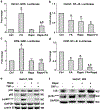
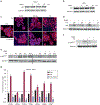
Glucocorticoids have excellent therapeutic properties; however, they cause significant adverse atrophogenic effects. The mTORC1 inhibitor REDD1 has been recently identified as a key mediator of glucocorticoid-induced atrophy. We performed computational screening of a connectivity map database to identify putative REDD1 inhibitors. The top selected candidates included rapamycin, which was unexpected because it inhibits pro-proliferative mTOR signaling. Indeed, rapamycin inhibited REDD1 induction by glucocorticoids dexamethasone, clobetasol propionate, and fluocinolone acetonide in keratinocytes, lymphoid cells, and mouse skin. We also showed blunting of glucocorticoid-induced REDD1 induction by either catalytic inhibitor of mTORC1/2 (OSI-027) or genetic inhibition of mTORC1, highlighting role of mTOR in glucocorticoid receptor signaling. Moreover, rapamycin inhibited glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation, nuclear translocation, and loading on glucocorticoid-responsive elements in REDD1 promoter. Using microarrays, we quantified a global effect of rapamycin on gene expression regulation by fluocinolone acetonide in human keratinocytes. Rapamycin inhibited activation of glucocorticoid receptor target genes yet enhanced the repression of pro-proliferative and proinflammatory genes. Remarkably, rapamycin protected skin against glucocorticoid-induced atrophy but had no effect on the glucocorticoid anti-inflammatory activity in different in vivo models, suggesting the clinical potential of combining rapamycin with glucocorticoids for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
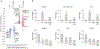

Similar articles
-
PI3K inhibitors protect against glucocorticoid-induced skin atrophy.EBioMedicine. 2019 Mar;41:526-537. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.055. Epub 2019 Feb 5. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30737086 Free PMC article.
-
REDD1 functions at the crossroads between the therapeutic and adverse effects of topical glucocorticoids.EMBO Mol Med. 2015 Jan;7(1):42-58. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404601. EMBO Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25504525 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Approach to Safer Glucocorticoid Receptor-Targeted Anti-lymphoma Therapy via REDD1 (Regulated in Development and DNA Damage 1) Inhibition.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Sep;19(9):1898-1908. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-1111. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32546661 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Sensor REDD1 in Cancer and Inflammation: Friend or Foe?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 26;23(17):9686. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179686. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The long winding road to the safer glucocorticoid receptor (GR) targeting therapies.Oncotarget. 2022 Feb 18;13:408-424. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28191. eCollection 2022. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 35198100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Anti-Cancer Activity of the Novel Selective Glucocorticoid Receptor Agonists of the Phenylethanolamine Series.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 15;25(16):8904. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168904. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201590 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Skin Atrophy: The Old and the New.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020 Dec 30;13:1041-1050. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S224211. eCollection 2020. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 33408495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDK7 blockade suppresses super-enhancer-associated oncogenes in bladder cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Aug;44(4):871-887. doi: 10.1007/s13402-021-00608-x. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33905040
-
Proteomic Changes during the Dermal Toxicity Induced by Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom in HaCaT Human Keratinocyte.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 27;13(5):311. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050311. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925349 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the glucocorticoid receptor chaperone FKBP51 prevents glucocorticoid-induced skin atrophy.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 5;9(78):34772-34783. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26194. eCollection 2018 Oct 5. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30410676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Britto FA, Begue G, Rossano B, Docquier A, Vernus B, Sar C, et al. REDD1 deletion prevents dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2014;307(11):E983–93. - PubMed
-
- De Bosscher K, Beck IM, Haegeman G. Classic glucocorticoids versus nonsteroidal glucocorticoid receptor modulators: survival of the fittest regulator of the immune system? Brain Behav Immun 2010;24:1035–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

