Protein-nucleic acid interactions of LINE-1 ORF1p
- PMID: 29596909
- PMCID: PMC6428221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.03.019
Protein-nucleic acid interactions of LINE-1 ORF1p
Abstract
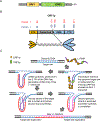
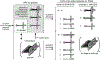
Long interspersed nuclear element 1 (LINE-1 or L1) is the dominant retrotransposon in mammalian genomes. L1 encodes two proteins ORF1p and ORF2p that are required for retrotransposition. ORF2p functions as the replicase. ORF1p is a coiled coil-mediated trimeric, high affinity RNA binding protein that packages its full- length coding transcript into an ORF2p-containing ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex, the retrotransposition intermediate. ORF1p also is a nucleic acid chaperone that presumably facilitates the proposed nucleic acid remodeling steps involved in retrotransposition. Although detailed mechanistic understanding of ORF1p function in this process is lacking, recent studies showed that the rate at which ORF1p can form stable nucleic acid-bound oligomers in vitro is positively correlated with formation of an active L1 RNP as assayed in vivo using a cell culture-based retrotransposition assay. This rate was sensitive to minor amino acid changes in the coiled coil domain, which had no effect on nucleic acid chaperone activity. Additional studies linking the complex nucleic acid binding properties to the conformational changes of the protein are needed to understand how ORF1p facilitates retrotransposition.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

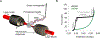
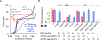
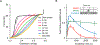
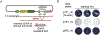
References
-
- Furano AV, The biological properties and evolutionary dynamics of mammalian LINE-1 retrotransposons, Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol 64 (2000) 255–294. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, et al., Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome, Nature 409 (6822) (2001) 860–921. - PubMed
-
- Esnault C, Maestre J, Heidmann T, Human LINE retrotransposons generate processed pseudogenes, Nat. Genet 24 (4) (2000) 363–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

