2-O, 3-O desulfated heparin mitigates murine chemotherapy- and radiation-induced thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 29599195
- PMCID: PMC5894257
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017013672
2-O, 3-O desulfated heparin mitigates murine chemotherapy- and radiation-induced thrombocytopenia
Erratum in
-
Tkaczynski E, Arulselvan A, Tkaczynski J, et al. 2-O, 3-O desulfated heparin mitigates murine chemotherapy- and radiation-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2018;2(7):754-761.Blood Adv. 2018 May 22;2(10):1129. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018020461. Blood Adv. 2018. PMID: 29776985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
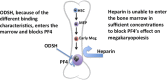
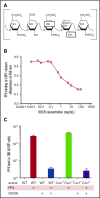
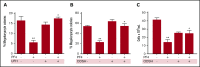
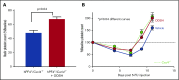
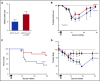
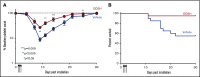
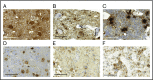
Thrombocytopenia is a significant complication of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Platelet factor 4 (PF4; CXCL4) is a negative paracrine of megakaryopoiesis. We have shown that PF4 levels are inversely related to steady-state platelet counts, and to the duration and severity of chemotherapy- and radiation-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT and RIT, respectively). Murine studies suggest that blocking the effect of PF4 improves megakaryopoiesis, raising nadir platelet counts and shortening the time to platelet count recovery. We examined the ability of 2-O, 3-O desulfated heparin (ODSH), a heparin variant with little anticoagulant effects, to neutralize PF4's effects on megakaryopoiesis. Using megakaryocyte colony assays and liquid cultures, we show that ODSH restored megakaryocyte proliferation in PF4-treated Cxcl4-/- murine and human CD34+-derived megakaryocyte cultures (17.4% megakaryocyte colonies, P < .01 compared with PF4). In murine CIT and RIT models, ODSH, started 24 hours after injury, was examined for the effect on hematopoietic recovery demonstrating higher platelet count nadirs (9% ± 5% treated vs 4% ± 4% control) and significantly improved survival in treated animals (73% treated vs 36% control survival). Treatment with ODSH was able to reduce intramedullary free PF4 concentrations by immunohistochemical analysis. In summary, ODSH mitigated CIT and RIT in mice by neutralizing the intramedullary negative paracrine PF4. ODSH, already in clinical trials in humans as an adjuvant to chemotherapy, may be an important, clinically relevant therapeutic for CIT and RIT.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of platelet factor 4 in radiation-induced thrombocytopenia.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Aug 1;80(5):1533-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.03.039. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 21740995 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of PF4/H multimolecular complex formation with a minimally anticoagulant heparin (ODSH).Thromb Haemost. 2012 Apr;107(4):717-25. doi: 10.1160/TH11-11-0795. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22318669 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet factor 4 is a negative autocrine in vivo regulator of megakaryopoiesis: clinical and therapeutic implications.Blood. 2007 Aug 15;110(4):1153-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-067116. Epub 2007 May 10. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17495129 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: an autoimmune disorder regulated through dynamic autoantigen assembly/disassembly.J Clin Apher. 2007 Feb;22(1):31-6. doi: 10.1002/jca.20109. J Clin Apher. 2007. PMID: 17285619 Review.
-
Heparins with reduced anti-coagulant activity reduce myocardial reperfusion injury.Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2011 May;6(2):148-57. doi: 10.2174/157489011795933855. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21453252 Review.
Cited by
-
Activating SRC/MAPK signaling via 5-HT1A receptor contributes to the effect of vilazodone on improving thrombocytopenia.Elife. 2024 Apr 4;13:RP94765. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94765. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38573820 Free PMC article.
-
Heparan Sulfate Mimetics in Cancer Therapy: The Challenge to Define Structural Determinants and the Relevance of Targets for Optimal Activity.Molecules. 2018 Nov 8;23(11):2915. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112915. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30413079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical impact of glycans in platelet and megakaryocyte biology.Blood. 2022 Jun 2;139(22):3255-3263. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009303. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35015813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UHPLC/MS-Based Serum Metabolomics Reveals the Mechanism of Radiation-Induced Thrombocytopenia in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 20;23(14):7978. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147978. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887324 Free PMC article.
-
Caulis Polygoni Multiflori Accelerates Megakaryopoiesis and Thrombopoiesis via Activating PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK Signaling Pathways.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;15(10):1204. doi: 10.3390/ph15101204. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bick RL, Strauss JF, Frenkel EP. Thrombosis and hemorrhage in oncology patients. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1996;10(4):875-907. - PubMed
-
- Dicarlo A, Kaminski JM, Hatchett R, Maidment BW. Role of thrombocytopenia in radiation-induced mortality and review of therapeutic approaches targeting platelet regeneration after radiation exposure. J Radiat Oncol. 2016;5(1):19-32.
-
- Dainiak N, Waselenko JK, Armitage JO, MacVittie TJ, Farese AM. The hematologist and radiation casualties. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2003;2003:473-496. - PubMed
-
- Mettler FA Jr, Voelz GL. Major radiation exposure--what to expect and how to respond. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(20):1554-1561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

