Molecular mechanism of extreme mechanostability in a pathogen adhesin
- PMID: 29599244
- PMCID: PMC6451932
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aar2094
Molecular mechanism of extreme mechanostability in a pathogen adhesin
Abstract
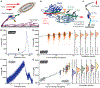
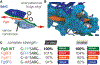
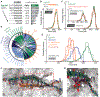
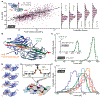
High resilience to mechanical stress is key when pathogens adhere to their target and initiate infection. Using atomic force microscopy-based single-molecule force spectroscopy, we explored the mechanical stability of the prototypical staphylococcal adhesin SdrG, which targets a short peptide from human fibrinogen β. Steered molecular dynamics simulations revealed, and single-molecule force spectroscopy experiments confirmed, the mechanism by which this complex withstands forces of over 2 nanonewtons, a regime previously associated with the strength of a covalent bond. The target peptide, confined in a screwlike manner in the binding pocket of SdrG, distributes forces mainly toward the peptide backbone through an intricate hydrogen bond network. Thus, these adhesins can attach to their target with exceptionally resilient mechanostability, virtually independent of peptide side chains.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
Comment in
-
Force matters in hospital-acquired infections.Science. 2018 Mar 30;359(6383):1464-1465. doi: 10.1126/science.aat3764. Science. 2018. PMID: 29599229 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ponnuraj K et al., A “dock, lock, and latch” Structural Model for a Staphylococcal Adhesin Binding to Fibrinogen. Cell. 115, 217–228 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

