Clinical Utility of Cell-Free DNA for the Detection of ALK Fusions and Genomic Mechanisms of ALK Inhibitor Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 29599410
- PMCID: PMC6157019
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2588
Clinical Utility of Cell-Free DNA for the Detection of ALK Fusions and Genomic Mechanisms of ALK Inhibitor Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene fusions benefit from treatment with ALK inhibitors (ALKi). Analysis of cell-free circulating tumor DNA (cfDNA) may provide a noninvasive way to identify ALK fusions and actionable resistance mechanisms without an invasive biopsy.Patients and Methods: The Guardant360 (G360; Guardant Health) deidentified database of NSCLC cases was queried to identify 88 consecutive patients with 96 plasma-detected ALK fusions. G360 is a clinical cfDNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) test that detects point mutations, select copy number gains, fusions, insertions, and deletions in plasma.Results: Identified fusion partners included EML4 (85.4%), STRN (6%), and KCNQ, KLC1, KIF5B, PPM1B, and TGF (totaling 8.3%). Forty-two ALK-positive patients had no history of targeted therapy (cohort 1), with tissue ALK molecular testing attempted in 21 (5 negative, 5 positive, and 11 tissue insufficient). Follow-up of 3 of the 5 tissue-negative patients showed responses to ALKi. Thirty-one patients were tested at known or presumed ALKi progression (cohort 2); 16 samples (53%) contained 1 to 3 ALK resistance mutations. In 13 patients, clinical status was unknown (cohort 3), and no resistance mutations or bypass pathways were identified. In 6 patients with known EGFR-activating mutations, an ALK fusion was identified on progression (cohort 4; 4 STRN, 1 EML4; one both STRN and EML4); five harbored EGFR T790M.Conclusions: In this cohort of cfDNA-detected ALK fusions, we demonstrate that comprehensive cfDNA NGS provides a noninvasive means of detecting targetable alterations and characterizing resistance mechanisms on progression. Clin Cancer Res; 24(12); 2758-70. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
Figures


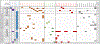
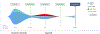
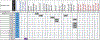

References
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. September 3 2009;361(10):947–957. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. February 2010;11(2):121–128. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. March 2012;13(3):239–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

