Grazer-induced transcriptomic and metabolomic response of the chain-forming diatom Skeletonema marinoi
- PMID: 29599523
- PMCID: PMC5955879
- DOI: 10.1038/s41396-018-0094-0
Grazer-induced transcriptomic and metabolomic response of the chain-forming diatom Skeletonema marinoi
Abstract
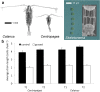
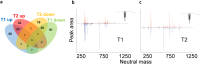
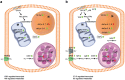
Diatoms and copepods are main actors in marine food webs. The prey-predator interactions between them affect bloom dynamics, shape marine ecosystems and impact the energy transfer to higher trophic levels. Recently it has been demonstrated that the presence of grazers may affect the diatom prey beyond the direct effect of grazing. Here, we investigated the response of the chain-forming centric diatom Skeletonema marinoi to grazer cues, including changes in morphology, gene expression and metabolic profile. S. marinoi cells were incubated with Calanus finmarchicus or with Centropages typicus and in both cases responded by reducing the chain length, whereas changes in gene expression indicated an activation of stress response, changes in the lipid and nitrogen metabolism, in cell cycle regulation and in frustule formation. Transcripts linked to G protein-coupled receptors and to nitric oxide synthesis were differentially expressed suggesting involvement of these signalling transduction pathways in the response. Downregulation of a lipoxygenase in the transcriptomic data and of its products in the metabolomic data also indicate an involvement of oxylipins. Our data contribute to a better understanding of the gene function in diatoms, providing information on the nature of genes implicated in the interaction with grazers, a crucial process in marine ecosystems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
De Novo Transcriptome Assembly and Gene Expression Profiling of the Copepod Calanus helgolandicus Feeding on the PUA-Producing Diatom Skeletonema marinoi.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jul 27;18(8):392. doi: 10.3390/md18080392. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32727111 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the oxylipin-producing diatom Skeletonema marinoi on gene expression levels of the calanoid copepod Calanus sinicus.Mar Genomics. 2015 Dec;24 Pt 1:89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Mar Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25666254
-
Insights into the transcriptome of the marine copepod Calanus helgolandicus feeding on the oxylipin-producing diatom Skeletonema marinoi.Harmful Algae. 2014 Jan;31:153-162. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Harmful Algae. 2014. PMID: 28040104
-
Toxigenic effects of diatoms on grazers, phytoplankton and other microbes: a review.Ecotoxicology. 2010 Mar;19(3):493-511. doi: 10.1007/s10646-009-0434-y. Ecotoxicology. 2010. PMID: 19924531 Review.
-
Multiple Roles of Diatom-Derived Oxylipins within Marine Environments and Their Potential Biotechnological Applications.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jun 30;18(7):342. doi: 10.3390/md18070342. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32629777 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Algal blooms in the ocean: hot spots for chemically mediated microbial interactions.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024 Mar;22(3):138-154. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00975-2. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 37833328 Review.
-
First regional reference database of northern Adriatic diatom transcriptomes.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 13;14(1):16209. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67043-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39003315 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing regulates 'swim-or-stick' lifestyle in the phycosphere.Environ Microbiol. 2020 Nov;22(11):4761-4778. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15228. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32896070 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and metabolome analyses of cold and darkness-induced pellicle cysts of Scrippsiella trochoidea.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jul 10;22(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07840-7. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34246248 Free PMC article.
-
Costs and benefits of predator-induced defence in a toxic diatom.Proc Biol Sci. 2022 Apr 13;289(1972):20212735. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2021.2735. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Proc Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35414232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calbet A. Mesozooplankton grazing effect on primary production: a global comparative analysis in marine ecosystems. Limnol Oceanogr. 2001;46:1824–30. doi: 10.4319/lo.2001.46.7.1824. - DOI
-
- Calbet A, Landry MR. Phytoplankton growth, microzooplankton grazing, and carbon cycling in marine systems. Limnol Oceanogr. 2004;49:51–57. doi: 10.4319/lo.2004.49.1.0051. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

