Interbrain cortical synchronization encodes multiple aspects of social interactions in monkey pairs
- PMID: 29599529
- PMCID: PMC5876380
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-22679-x
Interbrain cortical synchronization encodes multiple aspects of social interactions in monkey pairs
Abstract
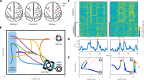
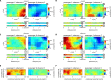
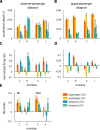
While it is well known that the primate brain evolved to cope with complex social contingencies, the neurophysiological manifestation of social interactions in primates is not well understood. Here, concurrent wireless neuronal ensemble recordings from pairs of monkeys were conducted to measure interbrain cortical synchronization (ICS) during a whole-body navigation task that involved continuous social interaction of two monkeys. One monkey, the passenger, was carried in a robotic wheelchair to a food dispenser, while a second monkey, the observer, remained stationary, watching the passenger. The two monkeys alternated the passenger and the observer roles. Concurrent neuronal ensemble recordings from the monkeys' motor cortex and the premotor dorsal area revealed episodic occurrence of ICS with probability that depended on the wheelchair kinematics, the passenger-observer distance, and the passenger-food distance - the social-interaction factors previously described in behavioral studies. These results suggest that ICS represents specific aspects of primate social interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Wireless Cortical Brain-Machine Interface for Whole-Body Navigation in Primates.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 3;6:22170. doi: 10.1038/srep22170. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26938468 Free PMC article.
-
The Computational and Neural Basis of Rhythmic Timing in Medial Premotor Cortex.J Neurosci. 2017 Apr 26;37(17):4552-4564. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0367-17.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28336572 Free PMC article.
-
Coding of Self and Other's Future Choices in Dorsal Premotor Cortex during Social Interaction.Cell Rep. 2018 Aug 14;24(7):1679-1686. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.030. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30110624
-
Role of the social actor during social interaction and learning in human-monkey paradigms.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019 Jul;102:242-250. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 6. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019. PMID: 31071362 Review.
-
Information processing for motor control in primate premotor cortex.Behav Brain Res. 1994 Apr 18;61(2):135-42. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(94)90154-6. Behav Brain Res. 1994. PMID: 8037861 Review.
Cited by
-
Improving scalability in systems neuroscience.Neuron. 2021 Jun 2;109(11):1776-1790. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.03.025. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 33831347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlated Neural Activity and Encoding of Behavior across Brains of Socially Interacting Animals.Cell. 2019 Jul 11;178(2):429-446.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.022. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31230711 Free PMC article.
-
Directed coupling in multi-brain networks underlies generalized synchrony during social exchange.Neuroimage. 2022 May 15;252:119038. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119038. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Neuroimage. 2022. PMID: 35231631 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous functional MRI of two awake marmosets.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 16;12(1):6608. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26976-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34785685 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved features of anterior cingulate networks support observational learning across species.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019 Dec;107:215-228. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.09.009. Epub 2019 Sep 8. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019. PMID: 31509768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

