Correlation between serum vitamin B12 level and peripheral neuropathy in atrophic gastritis
- PMID: 29599609
- PMCID: PMC5871829
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i12.1343
Correlation between serum vitamin B12 level and peripheral neuropathy in atrophic gastritis
Abstract
Aim: To explore the correlation between serum vitamin B12 level and peripheral neuropathy in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG).
Methods: A total of 593 patients diagnosed with chronic gastritis by gastroscopy and pathological examination from September 2013 to September 2016 were selected for this study. The age of these patients ranged within 18- to 75-years-old. Blood pressure, height and weight were measured in each patient, and the body mass index value was calculated. Furthermore, gastric acid, serum gastrin, serum vitamin and serum creatinine tests were performed, and peripheral nerve conduction velocity and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) were detected. In addition, the type of gastritis was determined by gastroscopy. The above factors were used as independent variables to analyze chronic gastritis with peripheral neuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency risk factors, and to analyze the relationship between vitamin B12 levels and peripheral nerve conduction velocity. In addition, in the treatment of CAG on the basis of vitamin B12, patients with peripheral neuropathy were observed.
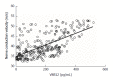
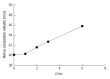
Results: Age, H. pylori infection, CAG, vitamin B9 and vitamin B12 were risk factors for the occurrence of peripheral nerve degeneration. Furthermore, CAG and H. pylori infection were risk factors for chronic gastritis associated with vitamin B12 deficiency. Serum vitamin B12 level was positively correlated with sensory nerve conduction velocity in the tibial nerve (R = 0.463). After vitamin B12 supplementation, patients with peripheral neuropathy improved.
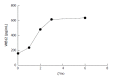
Conclusion: Serum vitamin B12 levels in patients with chronic gastritis significantly decreased, and the occurrence of peripheral neuropathy had a certain correlation. CAG and H. pylori infection are risk factors for vitamin B12 deficiency and peripheral neuropathy. When treating CAG, vitamin B12 supplementation can significantly reduce peripheral nervous system lesions. Therefore, the occurrence of peripheral neuropathy associated with vitamin B12 deficiency may be considered in patients with CAG. Furthermore, the timely supplementation of vitamin B12 during the clinical treatment of CAG can reduce or prevent peripheral nervous system lesions.
Keywords: Chronic atrophic gastritis; Chronic gastritis; Peripheral neuropathy; Vitamin B12.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: We declare that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Mescoli C, Gallo Lopez A, Taxa Rojas L, Jove Oblitas W, Fassan M, Rugge M. Gastritis staging as a clinical priority. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30:125–129. - PubMed
-
- Nomura S, Ida K, Terao S, Adachi K, Kato T, Watanabe H, Shimbo T; Research Group for Establishment of Endoscopic Diagnosis of Chronic Gastritis. Endoscopic diagnosis of gastric mucosal atrophy: multicenter prospective study. Dig Endosc. 2014;26:709–719. - PubMed
-
- Toh BH, Chan J, Kyaw T, Alderuccio F. Cutting edge issues in autoimmune gastritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012;42:269–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical