The effectiveness of alitretinoin for the treatment of chronic hand eczema: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 29599698
- PMCID: PMC5870332
The effectiveness of alitretinoin for the treatment of chronic hand eczema: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Alitretinoin is a new oral retinoid authorized for use in grownups that have severe chronic hand eczema (CHE). A comprehensive search to solicit all studies of alitretinoin for the treatment of CHE. A comprehensive search to solicit all studies of alitretinoin for the treatment of CHE including randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or uncontrolled trials, re-treatment studies, open-label studies, or observational studies, along with case series of 10 or more participants. Physician global assessment (PGA), patient global assessment (PaGA) and modified total lesion symptom score (mTLSS) are the methods and outcomes criteria. Generated effect size and 95% confidence intervals were calculated for the outcomes. Heterogeneity and publication bias were also tested for all selected trials. When a noteworthy Q statistic (P < 0.1) demonstrates the heterogeneity crosswise over studies, an arbitrary impact model is used. On the other hand, a settled effect model is when heterogeneity is not shown. The initial search yielded 408 records of which 15 articles were selected. The 15 clinical trials included 3734 patients with CHE. Among alitretinoin-treated patients, the PGA effect size was directly proportional to the drug dosage, ranging from 40% to 69%, while the PaGA score ranged from 28.8% to 62.4%, and mTLSS ranged from 60.4% to 76.9%, much higher than placebo. A higher drug dose was about twice as effective as lower dose. The odds ratio for a better outcome with drug treatment taking duration into account was about 3-4 times that versus placebo. In conclusions, alitretinoin cleared lesions in about 50% of cases, particularly using a higher dose for a longer duration.
Keywords: Alitretinoin; chronic hand eczema; meta-analysis.
Figures
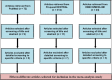



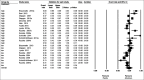

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Alitretinoin for Chronic Hand Eczema in Korean Patients.Ann Dermatol. 2016 Jun;28(3):364-70. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.364. Epub 2016 May 25. Ann Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27274636 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of alitretinoin depending on the concomitant use of topical corticosteroids in chronic hand eczema patients.J Dermatol. 2019 Nov;46(11):998-1005. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15071. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31535403
-
A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the efficacy and safety of alitretinoin (BAL4079) in the treatment of severe chronic hand eczema refractory to potent topical corticosteroid therapy.J Drugs Dermatol. 2014 Oct;13(10):1198-204. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25607554 Clinical Trial.
-
Alitretinoin for the treatment of severe chronic hand eczema.Health Technol Assess. 2010 May;14 Suppl 1:39-46. doi: 10.3310/hta14Suppl1/06. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20507802 Review.
-
Alitretinoin: in severe chronic hand eczema.Drugs. 2009 Aug 20;69(12):1625-34. doi: 10.2165/11202200-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19678713 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Alitretinoin Therapy in Korean Elderly Patients with Chronic Hand Eczema: A Retrospective Single Center Study.Ann Dermatol. 2019 Dec;31(6):595-600. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.6.595. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Ann Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 33911658 Free PMC article.
-
Alitretinoin Compliance in Patients with Chronic Hand Eczema.Ann Dermatol. 2021 Feb;33(1):46-51. doi: 10.5021/ad.2021.33.1.46. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Ann Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33911811 Free PMC article.
-
New Perspectives in the Management of Chronic Hand Eczema: Lessons from Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 27;25(1):362. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010362. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diepgen TL, Agner T, Aberer W, Berth-Jones J, Cambazard F, Elsner P, et al. Management of chronic hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis. 2007;57:203–10. - PubMed
-
- Held E, Skoet R, Johansen JD, Agner T. The hand eczema severity index (HECSI):A scoring system for clinical assessment of hand eczema. A study of inter- and intraobserver reliability. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152:302–7. - PubMed
-
- Cvetkovski RS, Zachariae R, Jensen H, Olsen J, Johansen JD, Agner T, et al. Quality of life and depression in a population of occupational hand eczema patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;54:106–11. - PubMed
-
- Van Coevorden AM, Coenraads PJ, Svensson A, Bavinck JN, Diepgen TL, Naldi L, et al. Overview of studies of treatments for hand eczema-the EDEN hand eczema survey. Br J Dermatol. 2004;151:446–51. - PubMed
-
- Bollag W, Ott F. Successful treatment of chronic hand eczema with oral 9-cis retinoic acid. Dermatology. 1999;199:308–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
