Ethnopharmacology-A Bibliometric Analysis of a Field of Research Meandering Between Medicine and Food Science?
- PMID: 29599720
- PMCID: PMC5862826
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00215
Ethnopharmacology-A Bibliometric Analysis of a Field of Research Meandering Between Medicine and Food Science?
Abstract
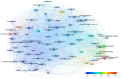
Background: The research into bioactive natural products of medicinal plants has a long tradition, but ethnopharmacology as a well-defined field of research has a relatively short history, only dating back 50 years. Aims: With the fast development of this field and its global importance especially in the fast developing economies of Asia it is timely to assess the most influential articles (as measured by citations) and to identify important drivers and research trends in this field. Methods: Scopus was searched to identify relevant articles which were assessed by all three authors. The 100 most cited articles were identified and analyzed. Bibliometric software (VOSviewer) was utilized to supplement the analysis and to generate a term map that visualized the citation patterns of the 100 articles containing different terms. Results: Forty-four of the 100 articles are reviews. On average, each of the 100 articles had 632 citations and since publication was cited 43 times annually. The four core journals were Journal of Ethnopharmacology (n = 17), Food Chemistry (n = 7), Life Sciences (n = 5), and Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (n = 4). Anti-oxidant effects appeared to be a recurring and highly cited topic, whereas the links into drug discovery and neuropharmacology seemed to be less strong. Numerous medicinal plants and functional foods were the foci of research, and the foci shifted when comparing pre-2000 and post-2000 publications (with the later involving a broader spectrum of plants and foods and a wider range of biological effects). Contributions largely came from Asia, and also from the Americas, Africa, and Oceania, besides Europe. Conclusion: We have identified and analyzed the 100 most-cited articles in ethnopharmacology. Within 50 years the field has gained a profile and while conventionally often linked to "traditional knowledge," drug discovery and some areas of pharmacology, this analysis highlights its emerging importance in the context of disease prevention (food science), but also the development of research driven by the needs and interests of the fast developing economies most notably of Asia.
Keywords: bibliometrics; ethnobotany; ethnomedicine; ethnopharmacology; folk medicine; medicinal plant; traditional medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Aggarwal B. B., Sundaram C., Malani N., Ichikawa H. (2007). Curcumin: the Indian solid gold, in The Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Uses of Curcumin in Health and Disease, eds Aggarwal B. B., Surh Y.-J., Shishodia S. (Berlin: Springer; ), 1–75. - PubMed
-
- Bisogno T., Hanuš L., De Petrocellis L., Tchilibon S., Ponde D. E., Brandi I., et al. . (2001). Molecular targets for cannabidiol and its synthetic analogues: effect on vanilloid VR1 receptors and on the cellular uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis of anandamide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 134, 845–852. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704327 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

