Age-Predicted Maximal Heart Rate in Recreational Marathon Runners: A Cross-Sectional Study on Fox's and Tanaka's Equations
- PMID: 29599724
- PMCID: PMC5862813
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00226
Age-Predicted Maximal Heart Rate in Recreational Marathon Runners: A Cross-Sectional Study on Fox's and Tanaka's Equations
Abstract
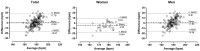
Age-based prediction equations of maximal heart rate (HRmax), such as the popular formulas Fox's 220-age, or Tanaka's 208-0.7 × age, have been widely used in various populations. Surprisingly, so far these equations have not been validated in marathon runners, despite the importance of the role of HRmax for training purposes in endurance running. The aim of the present study was to examine the validity of Fox and Tanaka equations in a large sample of women and men recreational marathon runners. Participants (n = 180, age 43.2 ± 8.5 years, VO2max 46.8 mL/min/kg, finishers in at least one marathon during the last year) performed a graded exercise test on a treadmill, where HRmax was measured. Measured HRmax correlated largely with age in the total sample (r = -0.50, p < 0.001), women (r = -0.60, p < 0.001) and men (r = -0.53, p < 0.001). In women, a large main effect of method on HRmax (p = 0.001, η2 = 0.294) was shown with measured HRmax lower than Fox-HRmax (-4.8 bpm; -8.4, -1.3) and Tanaka-HRmax (-4.9 bpm; -8.1, -1.8). In men, a moderate effect of assessment method on HRmax was found (p = 0.001, η2 = 0.066) with measured HRmax higher than Fox-HRmax (+2.8; 1.0, 4.6), Tanaka-HRmax higher than Fox-HRmax (+1.2; 0.7, 1.7). Based on these findings, it was concluded that Fox and Tanaka' formulas overestimated HRmax by ~5 bpm in women, whereas Fox underestimated HRmax in men by ~3 bpm. Thus, we recommend the further use of Tanaka's formula in men marathon runners. In addition, exercise physiologists and sport scientists should consider the observed differences among various assessment methods when performing exercise testing or prescribing training program relying on HR.
Keywords: age groups; cardiac rate; endurance runners; graded exercise test; sex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validity of Prediction Equations of Maximal Heart Rate in Physically Active Female Adolescents and the Role of Maturation.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Nov 13;55(11):735. doi: 10.3390/medicina55110735. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31766291 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of maximal heart rate using the prediction equations proposed by Karvonen and Tanaka.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2008 Nov;91(5):311-4. doi: 10.1590/s0066-782x2008001700005. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 19142375 English, Portuguese.
-
Age-predicted vs. measured maximal heart rate in young team sport athletes.Niger Med J. 2014 Jul;55(4):314-20. doi: 10.4103/0300-1652.137192. Niger Med J. 2014. PMID: 25114367 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Based Prediction of Maximal Heart Rate in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Res Q Exerc Sport. 2019 Sep;90(3):417-428. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2019.1615605. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2019. PMID: 31157608
-
Evidence and possible mechanisms of altered maximum heart rate with endurance training and tapering.Sports Med. 2000 Jan;29(1):13-26. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200029010-00002. Sports Med. 2000. PMID: 10688280 Review.
Cited by
-
Motivation in the Athens Classic Marathon: The Role of Sex, Age, and Performance Level in Greek Recreational Marathon Runners.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jul 17;16(14):2549. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16142549. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31319497 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in training activity post COVID-19 infection in recreational runners and cyclists.S Afr J Sports Med. 2022 Jan 1;34(1):v34i1a13758. doi: 10.17159/2078-516X/2022/v34i1a13758. eCollection 2022. S Afr J Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 36815935 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of Prediction Equations of Maximal Heart Rate in Physically Active Female Adolescents and the Role of Maturation.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Nov 13;55(11):735. doi: 10.3390/medicina55110735. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31766291 Free PMC article.
-
Are Activity Wrist-Worn Devices Accurate for Determining Heart Rate during Intense Exercise?Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Feb 15;10(2):254. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020254. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829748 Free PMC article.
-
Using Free-Living Heart Rate Data as an Objective Method to Assess Physical Activity: A Scoping Review and Recommendations by the INTERLIVE-Network Targeting Consumer Wearables.Sports Med. 2025 Feb;55(2):275-300. doi: 10.1007/s40279-024-02159-1. Epub 2025 Feb 2. Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 39893599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alemdaroglu U., Dündar U., Köklü Y., Asci A. (2012). Evaluation of aerobic capacity in soccer players: comparison of field and laboratory tests. Biol. Sport 29, 157–161. 10.5604/20831862.990468 - DOI
-
- Barboza J., Nogueira F. S., Paulucio D., Pompeu F. A. M. S. (2016). The validity of maximum heart rate predictions based on age for young men. Gazz. Med. Ital. 175, 154–157.
-
- Barboza J. A., Nogueira F. S., Pompeu F. A. M. S. (2017). A new accurate model to predict maximal heart rate. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 20, 23–28.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources