Brain GABA and Glutamate Concentrations Following Chronic Gabapentin Administration: A Convenience Sample Studied During Early Abstinence From Alcohol
- PMID: 29599727
- PMCID: PMC5862797
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00078
Brain GABA and Glutamate Concentrations Following Chronic Gabapentin Administration: A Convenience Sample Studied During Early Abstinence From Alcohol
Abstract
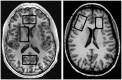
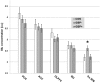
Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analog that may also affect glutamate (Glu) production, can normalize GABA and Glu tone during early abstinence from alcohol, effectively treating withdrawal symptoms and facilitating recovery. Using in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy, we tested the degree to which daily GBP alters regional brain GABA and Glu levels in short-term abstinent alcohol-dependent individuals. Regional metabolite levels were compared between 13 recently abstinent alcohol-dependent individuals who had received daily GBP for at least 1 week (GBP+) and 25 matched alcohol-dependent individuals who had not received GBP (GBP-). Magnetic resonance spectra from up to five different brain regions were analyzed to yield absolute GABA and Glu concentrations. GABA and Glu concentrations in the parieto-occipital cortex were not different between GBP- and GBP+. Glu levels in anterior cingulate cortex, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and basal ganglia did not differ between GBP- and GBP+. However, in a subgroup of individuals matched on age, sex, and abstinence duration, GBP+ had markedly lower Glu in the frontal white matter (WM) than GBP-, comparable to concentrations found in light/non-drinking controls. Furthermore, lower frontal WM Glu in GBP+ correlated with a higher daily GBP dose. Daily GBP treatment at an average of 1,600 mg/day for at least 1 week was not associated with altered cortical GABA and Glu concentrations during short-term abstinence from alcohol, but with lower Glu in frontal WM. GBP for the treatment of alcohol dependence may work through reducing Glu in WM rather than increasing cortical GABA.
Keywords: GABA; abstinence or withdrawal; alcohol dependence; alcohol use disorders; gabapentin; glutamate; magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Gabapentin on Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex GABA and Glutamate Levels and Their Associations With Abstinence in Alcohol Use Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Am J Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 1;178(9):829-837. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.20121757. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Am J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34256607 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Glutamate, GABA, and other cortical metabolite concentrations during early abstinence from alcohol and their associations with neurocognitive changes.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012 Sep 1;125(1-2):27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.03.012. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012. PMID: 22503310 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Glutamate and GABA Changes During Early Abstinence in Alcohol Dependence and Their Associations With Benzodiazepine Medication.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 5;12:656468. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.656468. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34290627 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin.Epilepsia. 1999;40 Suppl 5:S63-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1999.tb00921.x. Epilepsia. 1999. PMID: 10530696 Review.
-
Gabapentin-Associated Movement Disorders: A Literature Review.Medicines (Basel). 2023 Sep 6;10(9):52. doi: 10.3390/medicines10090052. Medicines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of intermittent theta burst to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on brain volumes and neurometabolites in people with alcohol use disorder: a preliminary investigation.Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Jul 22;19:1613993. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1613993. eCollection 2025. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40765765 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin increases expression of δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors.EBioMedicine. 2019 Apr;42:203-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 14. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30878595 Free PMC article.
-
Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, multimodal-MRI pilot study of gabapentin for co-occurring bipolar and cannabis use disorders.Addict Biol. 2022 Jan;27(1):e13085. doi: 10.1111/adb.13085. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Addict Biol. 2022. PMID: 34390300 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Brain Correlates of the Alcohol Use Disorder Pharmacotherapy Response: A Systematic Review of Neuroimaging Studies.Brain Sci. 2022 Mar 14;12(3):386. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12030386. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35326342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Gabapentin on Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex GABA and Glutamate Levels and Their Associations With Abstinence in Alcohol Use Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Am J Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 1;178(9):829-837. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.20121757. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Am J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34256607 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Gotz E, Feuerstein TJ, Lais A, Meyer DK. Effects of gabapentin on release of gamma-aminobutyric acid from slices of rat neostriatum. Arzneimittelforschung (1993) 43:636–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

