CD1d-Restricted Type II NKT Cells Reactive With Endogenous Hydrophobic Peptides
- PMID: 29599785
- PMCID: PMC5862807
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00548
CD1d-Restricted Type II NKT Cells Reactive With Endogenous Hydrophobic Peptides
Abstract
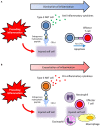
NKT cells belong to a distinct subset of T cells that recognize hydrophobic antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex class I-like molecules, such as CD1d. Because NKT cells stimulated by antigens can activate or suppress other immunocompetent cells through an immediate production of a large amount of cytokines, they are regarded as immunological modulators. CD1d-restricted NKT cells are classified into two subsets, namely, type I and type II. CD1d-restricted type I NKT cells express invariant T cell receptors (TCRs) and react with lipid antigens, including the marine sponge-derived glycolipid α-galactosylceramide. On the contrary, CD1d-restricted type II NKT cells recognize a wide variety of antigens, including glycolipids, phospholipids, and hydrophobic peptides, by their diverse TCRs. In this review, we focus particularly on CD1d-restricted type II NKT cells that recognize endogenous hydrophobic peptides presented by CD1d. Previous studies have demonstrated that CD1d-restricted type I NKT cells usually act as pro-inflammatory cells but sometimes behave as anti-inflammatory cells. It has been also demonstrated that CD1d-restricted type II NKT cells play opposite roles to CD1d-restricted type I NKT cells; thus, they function as anti-inflammatory or pro-inflammatory cells depending on the situation. In line with this, CD1d-restricted type II NKT cells that recognize type II collagen peptide have been demonstrated to act as anti-inflammatory cells in diverse inflammation-induction models in mice, whereas pro-inflammatory CD1d-restricted type II NKT cells reactive with sterol carrier protein 2 peptide have been demonstrated to be involved in the development of small vessel vasculitis in rats.
Keywords: CD1d; NKT cell; glycolipid; hydrophobic peptide; sulfatide.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

