[Overview of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in Morocco: results of the implementation of the program of clinical and biological diagnosis]
- PMID: 29599883
- PMCID: PMC5871254
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2017.28.185.11086
[Overview of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in Morocco: results of the implementation of the program of clinical and biological diagnosis]
Abstract
Introduction: X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a severe neurodegenerative disease, due to mutations in the ABCD1 gene. It manifests as a damage to the central and peripheral nervous system, adrenal insufficiency and testicular damage in children. Diagnosis is based on the determination of long-chain saturated fatty acids. Early diagnosis is essential because it defines treatment accessibility according to disease stage.
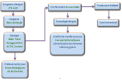
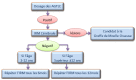
Methods: We implemented a X-ALD diagnostic test program in Morocco at the Children's Hospital and at the Central Laboratory for inherited and metabolic diseases in Rabat. The program was based around three priorities, namely: the recruitment of patients, diagnosis and awareness. Diagnosis is based on three protocols: a protocol for symptomatic cases, a protocol for asymptomatic cases and a protocol for heterozygous women.
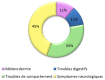
Results: During the first three years after implementation of our X-ALD diagnostic test program, we diagnosed the disease in seven families, with nine boys and three heterozygous women. All children were diagnosed with demyelinating brain. All heterozygous women were asymptomatic. Different symptom-based therapies were established.
Conclusion: X-ALD is a rare disease. Our diagnostic program has helped to diagnose a significant number of cases, hence its importance. Campaigns focused on raising awareness among health care professionals will enable a better understanding of the disease and a more accurate diagnosis as well as to improve access to health care for a higher number of patients.
Introduction: L'adrénoleucodystrophie liée à l'X (X-ALD) est une maladie neurodégénérative sévère, due à des mutations du gène ABCD1. Elle se manifeste par une atteinte du système nerveux central et périphérique, une insuffisance surrénalienne et une atteinte des testicules chez le garçon. Son diagnostic repose sur le dosage des Acides Gras à Très Longue Chaine. Le diagnostic précoce est d'une grande importance puisque il définit l'accessibilité aux traitements selon le stage de la maladie.
Méthodes: Nous avons mis en place un programme de diagnostic de l'X-ALD au Maroc au niveau de l'Hôpital d'enfants et du Laboratoire centrale des maladies héréditaires et du métabolisme de Rabat. Le programme s'articule sur trois axes à savoir : le recrutement des patients, le diagnostic et la sensibilisation. Le diagnostic s'effectue selon trois protocoles : un protocole pour les cas symptomatiques, un deuxième pour les cas asymptomatiques et un troisième pour les femmes hétérozygotes.
Résultats: Durant trois ans après la mise en place de notre programme de diagnostic de l'Adrénoleucodystrophie liée à l'X, nous avons diagnostiqué la maladie chez sept familles, avec neuf garçons et trois femmes hétérozygotes. Tous les enfants diagnostiqués présentaient la forme cérébrale démyélinisante. Toutes les femmes hétérozygotes étaient asymptomatiques. Une prise en charge thérapeutique a été mise place selon la symptomatologie de chaque cas.
Conclusion: l'X-ALD est une maladie rare. Notre programme de diagnostique a permis de diagnostiquer un nombre important de cas, ce qui montre son importance. Les compagnes de sensibilisation auprès des professionnels permettront de mieux comprendre la maladie et mieux la diagnostiquer et ainsi donner accès à un nombre plus élevé de patients.
Keywords: X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy; diagnosis; long-chain saturated fatty acids.
Figures
References
-
- Aubourg P. « Adrénoleucodystrophie liée à l'X ». Ann Endocrinol. 2007 Déc;68(6):403–411. - PubMed
-
- Aubourg P, et al. « Reversal of early neurologic and neuroradiologic manifestations of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy by bone marrow transplantation ». N Engl J Med. 1990 Juin;322(26):1860–1866. - PubMed
-
- Moser H W, Mahmood A, Raymond GV. « X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy ». Nat Clin PractNeurol. 2007 Mars;3(3):140–151. - PubMed
-
- Moser HW, et al. « Adrenoleukodystrophy: increased plasma content of saturated very long chain fatty acids ». Neurology. 1981 Oct;31(10):1241–1249. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources