Systems and WBANs for Controlling Obesity
- PMID: 29599941
- PMCID: PMC5823412
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1564748
Systems and WBANs for Controlling Obesity
Abstract
According to World Health Organization (WHO) estimations, one out of five adults worldwide will be obese by 2025. Worldwide obesity has doubled since 1980. In fact, more than 1.9 billion adults (39%) of 18 years and older were overweight and over 600 million (13%) of these were obese in 2014. 42 million children under the age of five were overweight or obese in 2014. Obesity is a top public health problem due to its associated morbidity and mortality. This paper reviews the main techniques to measure the level of obesity and body fat percentage, and explains the complications that can carry to the individual's quality of life, longevity and the significant cost of healthcare systems. Researchers and developers are adapting the existing technology, as intelligent phones or some wearable gadgets to be used for controlling obesity. They include the promoting of healthy eating culture and adopting the physical activity lifestyle. The paper also shows a comprehensive study of the most used mobile applications and Wireless Body Area Networks focused on controlling the obesity and overweight. Finally, this paper proposes an intelligent architecture that takes into account both, physiological and cognitive aspects to reduce the degree of obesity and overweight.
Figures


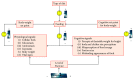
References
-
- School of Public Health (Harvard T.H. Chan) Obesity causes. October 2017, https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/obesity-prevention-source/obesity-causes/
-
- Kerry C. What is a healthy body fat percentage? October 2017, https://bodyfatloss.com/what-is-a-healthy-body-fat-percentage/
-
- World Health Organization. Noncommunicable diseases. October 2017, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs355/en/
-
- Sazonov E., Neuman M. R. Wearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and Applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

