Associations between biomarkers at discharge and co-morbidities and risk of readmission after community-acquired pneumonia: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 29600325
- PMCID: PMC5948264
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-018-3224-8
Associations between biomarkers at discharge and co-morbidities and risk of readmission after community-acquired pneumonia: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
To investigate whether hemoglobin, white blood cell count (WBC), urea, sodium, albumin, and C-reactive protein at discharge in patients hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) are associated with 30-day readmission. This study is a retrospective cohort study, which included all adult patients discharged after hospitalization for CAP from three Danish hospitals between January 2011 and July 2012. The outcome was all-cause, unplanned, 30-day readmission. Biomarker concentrations at discharge were transformed into binary variables by using either upper or lower quartiles as cut-off; the upper quartile was used for WBC, urea, and C-reactive protein, and the lower quartile was used for hemoglobin, sodium, and albumin. The study population consisted of 1149 patients. One hundred eighty-four (16.0%) patients were readmitted. Independent risk factors of readmission were WBC ≥ 10.6 cells × 109/L (hazard ratio 1.50; 95% CI, 1.07-2.11) and albumin <32 g/L (hazard ratio 1.78; 95% CI, 1.24-2.54) at discharge and the presence of ≥ 2 co-morbidities (hazard ratio 1.74; 95% CI, 1.15-2.64). When WBC, albumin, and co-morbidities were combined into a risk-stratification tool, there was a step-wise increase in risk of readmission for patients with 1, 2, or 3 risk factors with hazard ratios of 1.76 (95% CI, 1.25-2.49), 2.59 (95% CI, 1.71-3.93), and 6.15 (95% CI 3.33-11.38), respectively. WBC ≥ 10.6 cells × 109/L and albumin < 32 g/L at discharge and the presence of ≥ 2 co-morbidities were independently associated with increased risk of 30-day readmission.
Keywords: Biomarker; Community-acquired pneumonia; Readmission; Risk factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Gernot Rohde reports personal fees from Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Solvay, GSK, Essex Pharma, MSD, and Novartis for lectures including service on speakers’ bureaus outside the submitted work and personal fees from GSK for travel/accommodations/meeting expenses outside the submitted work. Pernille Ravn reports personal fees from MSD, invited speaker, personal fees from Abb Vie, invited speaker from Astellas, personal fees from CSL Behring, invited speaker, personal fees from Statens Serum Institute outside the submitted work The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the
Informed consent
Danish legislation does not require informed consent for register-based studies.
Figures


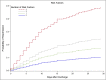
References
-
- Ewig S, Birkner N, Strauss R, Schaefer E, Pauletzki J, Bischoff H, et al. New perspectives on community-acquired pneumonia in 388 406 patients. Results from a nationwide mandatory performance measurement programme in healthcare quality. Thorax. 2009;64(12):1062–1069. doi: 10.1136/thx.2008.109785. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

