Serum YKL-40 as a biomarker for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal and mildly elevated ALT
- PMID: 29600444
- PMCID: PMC5976691
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-018-1136-2
Serum YKL-40 as a biomarker for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal and mildly elevated ALT
Abstract
Purpose: YKL-40 is a chitinase-like protein expressed in multiple tissues including liver and is reported as a fibrosis marker. This study aimed to determine whether YKL-40 could serve as a diagnostic marker for the assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal and mildly elevated ALT.
Methods: Six hundred and eighty-five patients with chronic hepatitis B infection were enrolled in this study from October 2013 to March 2016. All patients underwent liver biopsy and then staged based on Ishak histological system. Serum YKL-40 levels were measured by Human Magnetic Luminex Assays.
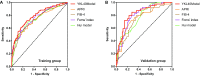
Results: Among chronic hepatitis B patients with normal and mildly elevated ALT, almost more than 30% of patients have significant liver fibrosis. Serum YKL-40 levels increased significantly in parallel with the progression of fibrosis in patients with ALT less than two times the upper limit of normal range (P < 0.0001). Multivariate analysis revealed that serum YKL-40, hyaluronic acid, PLT, and AST were independently associated with significant fibrosis. We established a novel YKL-40-based fibrosis model for patients with ALT less than two times the upper limit of normal range (ULN). YKL-40 model was superior to APRI, FIB-4, Forns' index, and Hui model for diagnosis of significant fibrosis in patients with ALT < 2ULN, with AUROCs of 0.786 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.726-0.846] in the training group, 0.831 (95%CI 0.752-0.910) in the validation group and 0.801 (95%CI 0.753-0.849) in the entire cohort.
Conclusion: Serum YKL-40 is a feasible biomarker of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients. YKL-40 model was superior to APRI, FIB-4, Forns' index and Hui model for diagnosis of significant fibrosis in patients with normal and mildly elevated ALT.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; Liver fibrosis; YKL-40.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the local ethics committee of Peking University First Hospital.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2013ZX10002005/China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases
- 2012ZX10002006/China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases
- 2013ZX10002004/China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases
- 2012ZX10005005/China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases
- D121100003912002/Project of Beijing Science and Technology Committee
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

