Antimicrobial Resistance: a One Health Perspective
- PMID: 29600770
- PMCID: PMC11633550
- DOI: 10.1128/microbiolspec.ARBA-0009-2017
Antimicrobial Resistance: a One Health Perspective
Abstract
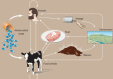
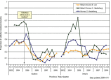
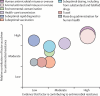
One Health is the collaborative effort of multiple health science professions to attain optimal health for people, domestic animals, wildlife, plants, and our environment. The drivers of antimicrobial resistance include antimicrobial use and abuse in human, animal, and environmental sectors and the spread of resistant bacteria and resistance determinants within and between these sectors and around the globe. Most of the classes of antimicrobials used to treat bacterial infections in humans are also used in animals. Given the important and interdependent human, animal, and environmental dimensions of antimicrobial resistance, it is logical to take a One Health approach when addressing this problem. This includes taking steps to preserve the continued effectiveness of existing antimicrobials by eliminating their inappropriate use and by limiting the spread of infection. Major concerns in the animal health and agriculture sectors are mass medication of animals with antimicrobials that are critically important for humans, such as third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones, and the long-term, in-feed use of medically important antimicrobials, such as colistin, tetracyclines, and macrolides, for growth promotion. In the human sector it is essential to prevent infections, reduce over-prescribing of antimicrobials, improve sanitation, and improve hygiene and infection control. Pollution from inadequate treatment of industrial, residential, and farm waste is expanding the resistome in the environment. Numerous countries and several international agencies have included a One Health approach within their action plans to address antimicrobial resistance. Necessary actions include improvements in antimicrobial use regulation and policy, surveillance, stewardship, infection control, sanitation, animal husbandry, and alternatives to antimicrobials. WHO recently has launched new guidelines on the use of medically important antimicrobials in food-producing animals, recommending that farmers and the food industry stop using antimicrobials routinely to promote growth and prevent disease in healthy animals. These guidelines aim to help preserve the effectiveness of antimicrobials that are important for human medicine by reducing their use in animals.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). 2014. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). 2013. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA.
-
- Fleming A. 1945. Penicillin. Nobel lecture.
-
- O’Neill J. 2016. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. The review on antimicrobial resistance. https://amr-review.org/.
-
- Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, Zaidi AKM, Wertheim HFL, Sumpradit N, Vlieghe E, Hara GL, Gould IM, Goossens H, Greko C, So AD, Bigdeli M, Tomson G, Woodhouse W, Ombaka E, Peralta AQ, Qamar FN, Mir F, Kariuki S, Bhutta ZA, Coates A, Bergstrom R, Wright GD, Brown ED, Cars O. 2013. Antibiotic resistance: the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect Dis 13:1057–1098 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70318-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

