Microbial degradation of Cold Lake Blend and Western Canadian select dilbits by freshwater enrichments
- PMID: 29602070
- PMCID: PMC6754826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.03.030
Microbial degradation of Cold Lake Blend and Western Canadian select dilbits by freshwater enrichments
Abstract
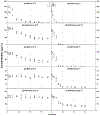
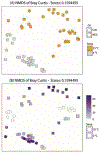
Treatability experiments were conducted to determine the biodegradation of diluted bitumen (dilbit) at 5 and 25 °C for 72 and 60 days, respectively. Microbial consortia obtained from the Kalamazoo River Enbridge Energy spill site were enriched on dilbit at both 5 (cryo) and 25 (meso) ºC. On every sampling day, triplicates were sacrificed and residual hydrocarbon concentrations (alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) were determined by GCMS/MS. The composition and relative abundance of different bacterial groups were identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis. While some physicochemical differences were observed between the two dilbits, their biodegradation profiles were similar. The rates and extent of degradation were greater at 25 °C. Both consortia metabolized 99.9% of alkanes; however, the meso consortium was more effective at removing aromatics than the cryo consortium (97.5 vs 70%). Known hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria were present in both consortia (Pseudomonas, Rhodococcus, Hydrogenophaga, Parvibaculum, Arthrobacter, Acidovorax), although their relative abundances depended on the temperatures at which they were enriched. Regardless of the dilbit type, the microbial community structure significantly changed as a response to the diminishing hydrocarbon load. Our results demonstrate that dilbit can be effectively degraded by autochthonous microbial consortia from sites with recent exposure to dilbit contamination.
Keywords: Biodegradation; Dilbit; Diluted bitumen; Microbial community structure; Non-conventional oil.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

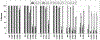

References
-
- Alberta energy, facts and statistics. January (2017) http://www.energy.alberta.ca/OilSands.
-
- Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers (CAPP), what are oil sands. February (2017) http://www.capp.ca/canadian-oil-and-natural-gas/oil-sands/what-are-oil-s....
-
- Crosby S, Fay R, Groark C, Kani A, Smith JR, Sullivan T, Pavia R Transporting Alberta oil sands products: defining the issues and assessing the risks US Department of Commerce (Ed.), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Technical Memorandum, NOAA technical memorandum; (2013)
-
- Meyer RF, Attanasi ED, Freeman PA Heavy Oil and Natural Bitumen Resources in Geological Basins of the World. Open File Report: 2007–1084 (2007)
-
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NAS) Spills of Diluted Bitumen from Pipelines: A Comparative Study of Environmental Fate, Effects, and Response The National Academies Press, Washington, DC: (2016)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

