LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma oxaliplatin resistance by targeting ABCC1 via miR-363
- PMID: 29602203
- PMCID: PMC5980138
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13605
LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma oxaliplatin resistance by targeting ABCC1 via miR-363
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Oxaliplatin Resistance by Targeting ABCC1 via miR-363.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Oct;29(20):e70908. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70908. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 41088835 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
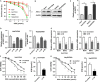
Emerging evidence has validated the vital role of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in the chemoresistance of cancer treatment. In the present study, we investigate the function of lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 on oxaliplatin (OXA) resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and discover the underlying molecular mechanism. Results revealed that lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 was up-regulated in oxaliplatin-resistant HCC tissue and cells using microarray analysis and RT-PCR. Meanwhile, ABCC1 protein was overexpressed in OXA-resistant HCC cells (Huh7/OXA and HepG2/OXA). In vitro, NR2F1-AS1 knockdown reduced the invasion, migration, drug-resistant gene (MDR1, MRP5, LRP1) and IC50 value in Huh7/OXA and HepG2/OXA cells. In vivo, NR2F1-AS1 knockdown decreased the tumour weight of HCC cells. Bioinformatics tools and luciferase reporter assay confirmed miR-363 targeted the 3'-UTR of NR2F1-AS1 and ABCC1 mRNA, presenting that NR2F1-AS1 promoted ABCC1 expression through endogenous sponging miR-363. In summary, results conclude that NR2F1-AS1 regulates HCC OXA resistance through targeting miR-363-ABCC1 pathway, providing a vital theoretic mechanism and therapeutic target for HCC chemoresistance.
Keywords: ABCC1; NR2F1-AS1; hepatocellular carcinoma; miR-363; oxaliplatin resistant.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures




References
-
- Innes H, Barclay ST, Hayes PC, et al. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients with hepatitis C and sustained viral response: role of the treatment regimen. J Hepatol. 2017;17:429‐437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

