Connectivity dynamics in typical development and its relationship to autistic traits and autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 29602272
- PMCID: PMC6045960
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24064
Connectivity dynamics in typical development and its relationship to autistic traits and autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
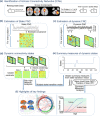
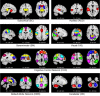
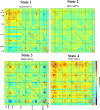
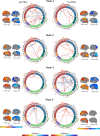
Recent advances in neuroimaging techniques have provided significant insights into developmental trajectories of human brain function. Characterizations of typical neurodevelopment provide a framework for understanding altered neurodevelopment, including differences in brain function related to developmental disorders and psychopathology. Historically, most functional connectivity studies of typical and atypical development operate under the assumption that connectivity remains static over time. We hypothesized that relaxing stationarity assumptions would reveal novel features of both typical brain development related to children on the autism spectrum. We employed a "chronnectomic" (recurring, time-varying patterns of connectivity) approach to evaluate transient states of connectivity using resting-state functional MRI in a population-based sample of 774 6- to 10-year-old children. Dynamic connectivity was evaluated using a sliding-window approach, and revealed four transient states. Internetwork connectivity increased with age in modularized dynamic states, illustrating an important pattern of connectivity in the developing brain. Furthermore, we demonstrated that higher levels of autistic traits and ASD diagnosis were associated with longer dwell times in a globally disconnected state. These results provide a roadmap to the chronnectomic organization of the developing brain and suggest that characteristics of functional brain connectivity are related to children on the autism spectrum.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; functional connectivity dynamics; independent component analysis; resting-state fMRI; typical development.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests in relation to the work presented.
Figures
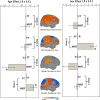
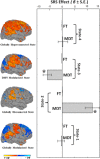
Comment in
-
Dissecting Static and Dynamic Functional Connectivity: Example From the Autism Spectrum.J Exp Neurosci. 2019 May 29;13:1179069519851809. doi: 10.1177/1179069519851809. eCollection 2019. J Exp Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31210734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agcaoglu, O. , Miller, R. , Damaraju, E. , Rashid, B. , Bustillo, J. , Cetin, M. , … Ford, J. (2017). Decreased hemispheric connectivity and decreased intra‐and inter‐hemisphere asymmetry of resting state functional network connectivity in schizophrenia. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 1–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baxter, A. J. , Brugha, T. S. , Erskine, H. E. , Scheurer, R. W. , Vos, T. , & Scott, J. G. (2015). The epidemiology and global burden of autism spectrum disorders. Psychological Medicine, 45(03), 601–613. - PubMed
-
- Bell, A. J. , & Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). An information‐maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Computation, 7(6), 1129–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

