Gold nanoparticles stabilize peptide-drug-conjugates for sustained targeted drug delivery to cancer cells
- PMID: 29602308
- PMCID: PMC5877385
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-018-0362-1
Gold nanoparticles stabilize peptide-drug-conjugates for sustained targeted drug delivery to cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Peptide-drug-conjugates (PDCs) are being developed as an effective strategy to specifically deliver cytotoxic drugs to cancer cells. However one of the challenges to their successful application is the relatively low stability of peptides in the blood, liver and kidneys. Since AuNPs seem to have a longer plasma half-life than PDCs, one approach to overcoming this problem would be to conjugate the PDCs to gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), as these have demonstrated favorable physico-chemical and safety properties for drug delivery systems. We set out to test whether PEG coated-AuNPs could provide a suitable platform for the non-covalent loading of pre-formed PDCs and whether this modification would affect the bioavailability of the PDCs and their cytotoxicity toward target cancer cells.
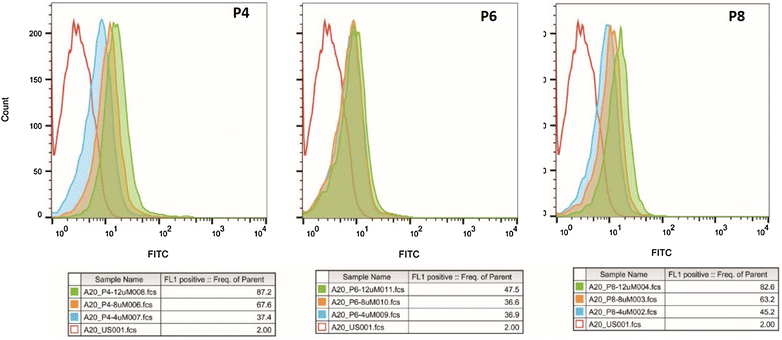
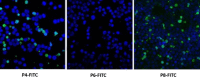
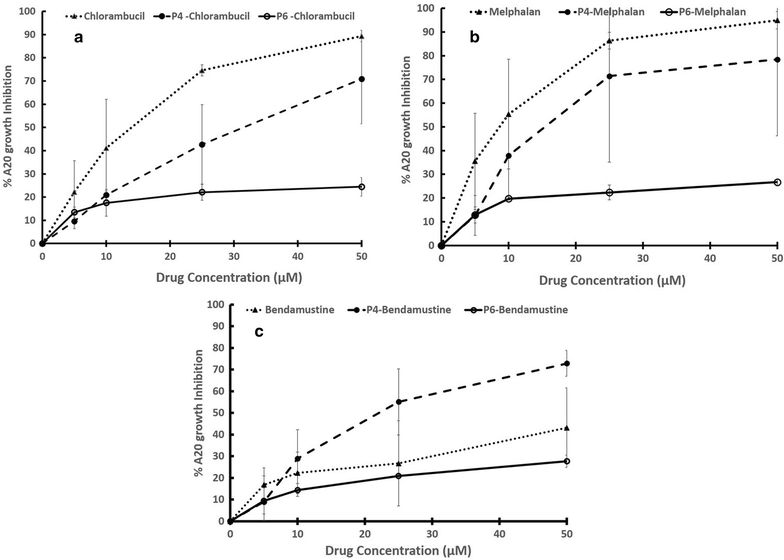
Methods: Peptides specifically internalized by A20 murine lymphoma cells were isolated from a phage library displaying 7mer linear peptides. Peptide specificity was validated by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. PDCs were synthesized containing a selected peptide (P4) and either chlorambucil (Chlor), melphalan (Melph) or bendamustine (Bend). Gold nanoparticles were sequentially coated with citrate, PEG-6000 and then PDC (PDC-PEG-AuNP). The physico-chemical properties of the coated particles were analyzed by electrophoresis, TEM, UV-VIS and FTIR. Stability of free and PDC-coated AuNP was determined.
Results: Biopanning of the phage library resulted in discovery of several novel peptides that internalized into A20 cells. One of these (P4) was used to synthesize PDCs containing either Chlor, Melph or Bend. All three PDCs specifically killed A20 target cells, however they had short half-lives ranging from 10.6 to 15.4 min. When coated to PEG-AuNPs, the half-lives were extended to 21.0-22.3 h. The PDC-PEG-AuNPs retained cytotoxicity towards the target cells. Moreover, whereas pre-incubation for 24 h of free PDCs almost completely abolished their cytotoxic activity, the PDC-PEG-AuNPs were still active even after 72 h pre-incubation.
Conclusions: Peptide-drug-conjugates hold potential for improving the target efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs, however their short half-lives may limit their application. This hurdle can be overcome by easily conjugating them to gold nanoparticles. This conjugation also opens up the possibility of developing slow release formulations of targeted drug delivery systems containing PDCs.
Keywords: Gold nanoparticles; Peptide drug conjugates; Phage display; Targeted drug delivery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticle: Peptide-Drug Conjugates for Targeted Drug Delivery.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2059:145-154. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9798-5_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31435919
-
A comparison of gold nanoparticle surface co-functionalization approaches using Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and the effect on stability, non-specific protein adsorption and internalization.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 May;62:710-8. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.02.003. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 26952476
-
Polymer decorated gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine conjugates.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Nov;249:386-399. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 28259207 Review.
-
Discovery of peptide drug carrier candidates for targeted multi-drug delivery into prostate cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2017 Nov 1;408:164-173. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.040. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28888997
-
Current progress and remaining challenges of peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs): next generation of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs)?J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Apr 22;23(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03277-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40259322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Colistin Conjugated with Chitosan-Capped Gold Nanoparticles as a Possible Formulation Applied in a Metered-Dose Inhaler.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 6;13(7):630. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070630. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061312 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Gold Nanoparticle-Based Combined Cancer Therapy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Aug 26;10(9):1671. doi: 10.3390/nano10091671. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32858957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Gold Nanoparticle Naproxen-Derived Conjugations in Ovarian Cancer.ACS Mater Au. 2023 Jun 9;3(5):483-491. doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialsau.3c00033. eCollection 2023 Sep 13. ACS Mater Au. 2023. PMID: 38089100 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Chlorambucil and Mercaptopurine Show Effective Anti-Cancer Effects in Mice Model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 29;18:8131-8141. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S438742. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38169995 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding cellular interactions with nanomaterials: towards a rational design of medical nanodevices.Nanotechnology. 2020 Mar 27;31(13):132002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab5bc8. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Nanotechnology. 2020. PMID: 31770746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

