The change in groin pain perception after transabdominal preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair with glue fixation: a prospective trial of a single surgeon's experience
- PMID: 29603008
- PMCID: PMC6132881
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-018-6178-0
The change in groin pain perception after transabdominal preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair with glue fixation: a prospective trial of a single surgeon's experience
Abstract
Background: Although inguinal hernia is one of the most common conditions requiring surgical treatment, no reliable information is available on the quality of life of patients with inguinal hernias before surgery. Additionally, patients with intense inguinal pain prior to surgery are more susceptible to postoperative chronic pain. In such cases, less invasive laparoscopic techniques can be used, allowing atraumatic mesh fixation to reduce postoperative pain. The aim of the study was to determine, whether these treatments for patients with preoperative pain would minimize upsetting experiences after surgery.
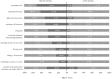
Materials and methods: Data were gathered prospectively from the National Hernia Repair Register for 146 patients who underwent TAPP repairs in the general surgery department (2013-2016). The demographic data were recorded, the pain intensity was determined and patients described the occurrence of pain during ten everyday activities.
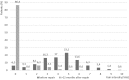
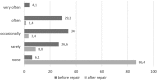
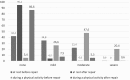
Results: The average surgery time was 56.4 min. The follow-up was 23.4 months. The pain before surgery was 4.28 and 12 months after surgery 0.38 (p < 0.001). Pain intensity before surgery was scored as 4.1, 4.3, and 4.9 among patients who had a hernia < 12 months, > 1 year, and > 5 years, respectively (p = 0.028). Twelve months after surgery, the pain was 0.26, 0.34, and 0.40 (p = 0.037), respectively. Patients < 40 years experienced pain before the surgery more often. The intensity of pre-/postoperative pain was significantly higher < 40 years (4.9/0.63) than > 60 years (3.8/0.29).
Conclusions: TAPP inguinal hernia repair with glue fixation significantly decreased the frequency and intensity of the pain compared to that experienced preoperatively. After TAPP repair, the influence of pain on basic everyday activities is substantially lower. Patients under 40 years of age experience frequent and intense pre- and postoperative pain. A longer hernia duration prior to surgery causes increased pre- and postoperative pain.
Keywords: Hernia repair; Laparoscopic; Pain; Preoperative; Quality of life; TAPP.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Mitura, Garnysz, Wyrzykowska, and Michalek have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A prospective, randomized comparison of long-term outcomes: chronic groin pain and quality of life following totally extraperitoneal (TEP) and transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair.Surg Endosc. 2013 Jul;27(7):2373-82. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2797-7. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Surg Endosc. 2013. PMID: 23389072 Clinical Trial.
-
International guidelines for groin hernia management.Hernia. 2018 Feb;22(1):1-165. doi: 10.1007/s10029-017-1668-x. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Hernia. 2018. PMID: 29330835 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective randomized comparison of testicular functions, sexual functions and quality of life following laparoscopic totally extra-peritoneal (TEP) and trans-abdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) inguinal hernia repairs.Surg Endosc. 2017 Mar;31(3):1478-1486. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-5142-0. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Surg Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27495344 Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing nonpenetrating vs mechanical mesh fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair.Am J Surg. 2016 Jan;211(1):239-249.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Am J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26316363
-
Comparison of postoperative chronic inguinal pain between the lichtenstein and laparoscopic techniques in the treatment of inguinal hernia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hernia. 2024 Oct;28(5):1537-1546. doi: 10.1007/s10029-024-03099-5. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Hernia. 2024. PMID: 39031236
Cited by
-
Cyanoacrylate mesh fixation for laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a prospective, multicenter, single-arm study.Surg Endosc. 2023 Dec;37(12):9105-9115. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10439-6. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37798529
-
Assessment of feasibility and safety of cyanoacrylate glue versus absorbable tacks for inguinal hernia mesh fixation. A prospective comparative study.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2023 Mar;18(1):90-98. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2022.119780. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2023. PMID: 37064566 Free PMC article.
-
The learning curve of laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a comparison of three inexperienced surgeons.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2021 Jun;16(2):336-346. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2020.100831. Epub 2020 Nov 15. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2021. PMID: 34136029 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of Lichtenstein repair vs the Valenti technique for inguinal hernia.Hernia. 2019 Jun;23(3):547-554. doi: 10.1007/s10029-019-01879-y. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Hernia. 2019. PMID: 30659397 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Outcomes of 207 totally extraperitoneal hernia repairs using self-fixation mesh.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 15;11(1):12507. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92063-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34131236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitura K, Romanczuk M. Redundant modifications of Lichtenstein technique in hernia repair—a descriptive study of practising surgeons. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2009;4:1–5.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

