Association between B-type natriuretic peptide and within-visit blood pressure variability
- PMID: 29604077
- PMCID: PMC6490113
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.22953
Association between B-type natriuretic peptide and within-visit blood pressure variability
Abstract
Background: Blood pressure variability (BPV) has been shown to predict cardiovascular events. Within-visit BPV is the simplest and easiest measure of BPV, but previous studies have shown conflicts as to whether within-visit BPV correlates with target organ damage. We aimed to evaluate whether within-visit BPV correlates with B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) in a general population.
Hypothesis: Within-visit BPV correlates with BNP in a general population.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study that included 633 individuals, randomly selected, age 45 to 99 years, registered in the primary care program from an urban medium-sized town. Patients were scheduled for a single-day visit that consisted of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Three blood pressure (BP) readings, 1 minute apart, were done, and within-visit BPV was determined as the coefficient of variation (CV) of the 3 BP measures. Our main outcome was to correlate BNP and within-visit BPV. A multivariable model was estimated using a generalized linear model to evaluate the independent effects of different variables on BNP levels.
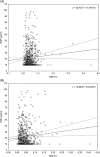
Results: The median age was 57 years. Median BNP was 16 pg/mL, and the median systolic and diastolic BP-CV were, respectively, 3.9% and 3.5%. There was a weak but positive correlation between BNP and both systolic BP-CV and diastolic BP-CV (r = 0.107 and P = 0.007 and r = 0.092 and P = 0.019, respectively). In multiple regression equation, systolic BP, diastolic BP-CV, body mass index, and estimated glomerular filtration rate were associated with BNP.
Conclusions: In the present study, there was a positive, albeit weak, correlation between within-visit BPV and BNP. In addition, diastolic BPV was associated with BNP even after adjustment for multiple confounders.
Keywords: Blood Pressure; Blood Pressure Variability; Brain Natriuretic Peptide.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between day-to-day variability in home blood pressure measurement and multiple organ function.Hypertens Res. 2022 Mar;45(3):474-482. doi: 10.1038/s41440-021-00818-8. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Hypertens Res. 2022. PMID: 34934161
-
Number of blood pressure measurements needed to estimate long-term visit-to-visit systolic blood pressure variability for predicting cardiovascular risk: a 10-year retrospective cohort study in a primary care clinic in Malaysia.BMJ Open. 2019 Apr 20;9(4):e025322. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025322. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31005918 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of visit-to-visit blood pressure variability for cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease with and without diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Apr 24;20(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01280-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33894788 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches for Evaluating Visit-to-Visit Blood Pressure Variability as a Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factor: A Scoping Review.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024 Aug 22;316:349-353. doi: 10.3233/SHTI240417. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024. PMID: 39176745
-
Association between different methods of assessing blood pressure variability and incident cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality: a systematic review.Age Ageing. 2020 Feb 27;49(2):184-192. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afz178. Age Ageing. 2020. PMID: 31985773
Cited by
-
Blood Pressure Variability and Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Acute ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: The Relation with Left Atrial Electromechanical Delay - A 1-Year Follow-Up Study.Pulse (Basel). 2020 Aug;8(1-2):57-65. doi: 10.1159/000507792. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Pulse (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32999879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grassi G, Seravalle G, Maloberti A, et al. Within‐visit BP variability, cardiovascular risk factors, and BP control in central and eastern Europe. J Hypertens. 2015;33:2250–2256. - PubMed
-
- Zhou TL, Kroon AA, Reesink KD, et al. Blood pressure variability in individuals with and without (pre)diabetes: the Maastricht Study. J Hypertens. 2018;36:259–267. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

