Uteroplacental insufficiency temporally exacerbates salt-induced hypertension associated with a reduced natriuretic response in male rat offspring
- PMID: 29604087
- PMCID: PMC6265551
- DOI: 10.1113/JP275655
Uteroplacental insufficiency temporally exacerbates salt-induced hypertension associated with a reduced natriuretic response in male rat offspring
Abstract
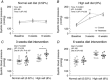
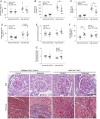
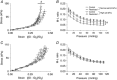
Low weight at birth increases the risk of developing chronic diseases in adulthood A diet that is high in salt is known to elevate blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular and kidney diseases The present study demonstrates that growth restricted male rats have a heightened sensitivity to high dietary salt, in the context of raised systolic blood pressure, reduced urinary sodium excretion and stiffer mesenteric resistance vessels Other salt-induced effects, such as kidney hyperfiltration, albuminuria and glomerular damage, were not exacerbated by being born small The present study demonstrates that male offspring born small have an increased cardiovascular susceptibility to high dietary salt, such that that minimizing salt intake is probably of particular benefit to this at-risk population ABSTRACT: Intrauterine growth restriction increases the risk of developing chronic diseases in adulthood. Lifestyle factors, such as poor dietary choices, may elevate this risk. We determined whether being born small increases the sensitivity to a dietary salt challenge, in the context of hypertension, kidney disease and arterial stiffness. Bilateral uterine vessel ligation or sham surgery (offspring termed Restricted and Control, respectively) was performed on 18-day pregnant Wistar Kyoto rats. Male offspring were allocated to receive a diet high in salt (8% sodium chloride) or remain on standard rat chow (0.52% sodium chloride) from 20 to 26 weeks of age for 6 weeks. Systolic blood pressure (tail-cuff), renal function (24 h urine excretions) and vascular stiffness (pressure myography) were assessed. Restricted males were born 15% lighter than Controls and remained smaller throughout the study. Salt-induced hypertension was exacerbated in Restricted offspring, reaching a peak systolic pressure of ∼175 mmHg earlier than normal weight counterparts. The natriuretic response to high dietary salt in Restricted animals was less than in Controls and may explain the early rise in arterial pressure. Growth restricted males allocated to a high salt diet also had increased passive arterial stiffness of mesenteric resistance arteries. Other aspects of renal function, including salt-induced hyperfiltration, albuminuria and glomerular damage, were not exacerbated by uteroplacental insufficiency. The present study demonstrates that male offspring exposed to uteroplacental insufficiency and born small have an increased sensitivity to salt-induced hypertension and arterial remodelling.
Keywords: blood pressure; developmental programming; growth restriction.
© 2018 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2018 The Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Appel LJ, Brands MW, Daniels SR, Karanja N, Elmer PJ, Sacks FM & American Heart A (2006). Dietary approaches to prevent and treat hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 47, 296–308. - PubMed
-
- Arribas SM, Briones AM, Bellingham C, Gonzalez MC, Salaices M, Liu K, Wang Y & Hinek A (2008). Heightened aberrant deposition of hard‐wearing elastin in conduit arteries of prehypertensive SHR is associated with increased stiffness and inward remodeling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295, H2299–H2307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

