Risk factors and mortality rate in premature babies with acute kidney injury
- PMID: 29604124
- PMCID: PMC6817040
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22441
Risk factors and mortality rate in premature babies with acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common morbidity in neonatal intensive care units and associated with poor outcome. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of AKI and provide a demographic data and risk factors associated with the mortality and morbidity.
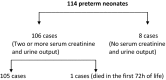
Methods: This is a retrospective study included 105 premature babies. Diagnosis of AKI was based on neonatal KDIGO classification criteria. The babies were stratified into two groups according to AKI status during the hospitalization. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of the AKI group were compared to non-AKI group.
Results: AKI occurred in 21 (20.0%) of 105 premature babies, and mortality rate in these babies was 61.9%. Lower gestational weeks, lower Apgar scores at 5 minutes, lower systolic blood pressures, and inotropic supports were independent risk factors for the development of AKI in preterm babies (P < .05, for each). Oliguria, preeclampsia/eclampsia, resuscitation at birth, lower diastolic blood pressure, patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), inotropic support, and furosemide treatment were associated with the mortality (P < .05, for each).
Conclusions: Prenatal risk factors and medical interventions are associated with AKI, and AKI is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Therefore, identification of AKI is very important in this vulnerable population and it should be performed as quickly as possible in all babies who are at high risk for developing of AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; neonatal intensive care unit; premature babies.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
References
-
- Lemons JA, Bauer CR, Oh W, et al. Very low birth weight outcomes of the National Institute of Child health and human development neonatal research network, January 1995 through December 1996. NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E1. - PubMed
-
- Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birth weight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196:147. e1‐147.e8. - PubMed
-
- Agras PI, Tarcan A, Baskin E, Cengiz N, Gurakan B, Saatci U. Acute renal failure in the neonatal period. Ren Fail. 2004;26:305‐309. - PubMed
-
- Hentschel R, Lodige B, Bulla M. Renal insufficiency in the neonatal period. Clin Nephrol. 1996;46:54‐58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical