Cysteine dioxygenase is essential for mouse sperm osmoadaptation and male fertility
- PMID: 29604178
- PMCID: PMC5992081
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14449
Cysteine dioxygenase is essential for mouse sperm osmoadaptation and male fertility
Abstract
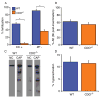
Sperm entering the epididymis are immotile and cannot respond to stimuli that will enable them to fertilize. The epididymis is a highly complex organ, with multiple histological zones and cell types that together change the composition and functional abilities of sperm through poorly understood mechanisms. Sperm take up taurine during epididymal transit, which may play antioxidant or osmoregulatory roles. Cysteine dioxygenase (CDO) is a critical enzyme for taurine synthesis. A previous study reported that male CDO-/- mice exhibit idiopathic infertility, prompting us to investigate the functions of CDO in male fertility. Immunoblotting and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of epididymal segments showed that androgen-dependent CDO expression was highest in the caput epididymidis. CDO-/- mouse sperm demonstrated a severe lack of in vitro fertilization ability. Acrosome exocytosis and tyrosine phosphorylation profiles in response to stimuli were normal, suggesting normal functioning of pathways associated with capacitation. CDO-/- sperm had a slight increase in head abnormalities. Taurine and hypotaurine concentrations in CDO-/- sperm decreased in the epididymal intraluminal fluid and sperm cytosol. We found no evidence of antioxidant protection against lipid peroxidation. However, CDO-/- sperm exhibited severe defects in volume regulation, swelling in response to the relatively hypo-osmotic conditions found in the female reproductive tract. Our findings suggest that epididymal CDO plays a key role in post-testicular sperm maturation, enabling sperm to osmoregulate as they transition from the male to the female reproductive tract, and provide new understanding of the compartmentalized functions of the epididymis.
Keywords: epididymal maturation; fertilization; sperm; taurine.
© 2018 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Cooper TG, Yeung CH. Acquisition of volume regulatory response of sperm upon maturation in the epididymis and the role of the cytoplasmic droplet. Microsc Res Tech. 2003;61:28–38. - PubMed
-
- Yeung CH, Wagenfeld A, Nieschlag E, Cooper TG. The cause of infertility of male c-ros tyrosine kinase receptor knockout mice. Biol Reprod. 2000;63:612–8. - PubMed
-
- Yeung CH, Sonnenberg-Riethmacher E, Cooper TG. Infertile spermatozoa of c-ros tyrosine kinase receptor knockout mice show flagellar angulation and maturational defects in cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Biol Reprod. 1999;61:1062–9. - PubMed
-
- Yeung CH, Anapolski M, Sipila P, Wagenfeld A, Poutanen M, Huhtaniemi I, Nieschlag E, Cooper TG. Sperm volume regulation: maturational changes in fertile and infertile transgenic mice and association with kinematics and tail angulation. Biol Reprod. 2002;67:269–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

