Investigational chemotherapy and novel pharmacokinetic mechanisms for the treatment of breast cancer brain metastases
- PMID: 29604436
- PMCID: PMC5997530
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.03.021
Investigational chemotherapy and novel pharmacokinetic mechanisms for the treatment of breast cancer brain metastases
Abstract
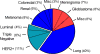
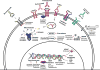
In women, breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosis and second most common cause of cancer death. More than half of breast cancer patients will develop metastases to the bone, liver, lung, or brain. Breast cancer brain metastases (BCBM) confers a poor prognosis, as current therapeutic options of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy rarely significantly extend life and are considered palliative. Within the realm of chemotherapy, the last decade has seen an explosion of novel chemotherapeutics involving targeting agents and unique dosage forms. We provide a historical overview of BCBM chemotherapy, review the mechanisms of new agents such as poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors, phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinaseinhibitors, estrogen pathway antagonists for hormone-receptor positive BCBM; tyrosine kinase inhibitors, antibodies, and conjugates for HER2+ BCBM; repurposed cytotoxic chemotherapy for triple negative BCBM; and the utilization of these new agents and formulations in ongoing clinical trials. The mechanisms of novel dosage formulations such as nanoparticles, liposomes, pegylation, the concepts of enhanced permeation and retention, and drugs utilizing these concepts involved in clinical trials are also discussed. These new treatments provide a promising outlook in the treatment of BCBM.
Keywords: 5-Azacitidine (PubMED CID: 9444); 5-Fluorouracil (PubMED CID: 3385); Abemaciclib (PubMED CID: 46220502); Afatinib (PubMED CID: 10184653); Alisertib (PubMED CID: 24471867); Alpelisib (PubMED CID: 56649450); Anastrozole (PubMED CID: 2187); Apitolisib (PubMED CID: 25254071); Bleomycin (PubMED CID: 5360373); Breast cancer brain metastases; Brilanestrant (PubMED CID: 56941241); Buparlisib (PubMED CID: 16654980); Cabozantinib (PubMED CID: 25102847); Capecitabine (PubMED CID: 60953); Carmustine (PubMED CID: 2578); Cisplatin (PubMED CID: 84691); Clinical trials; Cyclophosphamide (PubMED CID: 2907); Cytarabine (PubMED CID: 6253); Dactolisib (PubMED CID: 11977753); Daunorubicin (PubMED CID: 30323); Docetaxel (PubMED CID: 148124); Doxorubicin (PubMED CID: 31703); Elacestrant (PubMED CID: 23462301); Entinostat (PubMED CID: 4261); Eribulin (PubMED CID: 17755248); Estradiol (PubMED CID: 5757); Etirinotecan pegol (PubMED CID: 71300725); Etoposide (PubMED CID: 36462); Everolimus (PubMED CID: 18477728); Exemestane (PubMED CID: 60198); Fulvestrant (PubMED CID: 104741); Gemcitabine (PubMED CID: 60750); Goserelin (PubMED CID: 5311128); Ifosfamide (PubMED CID: 3690); Iniparib (PubMED CID: 9796068); Irinotecan (PubMED CID: 60838); Lapatinib (PubMED CID: 208908); Lenvatinib (PubMED CID: 9823820); Letrozole (PubMED CID: 3902); Leuprorelin (PubMED CID: 657181); Liposomes; Lomustine (PubMED CID: 3950); Methotrexate (PubMED CID: 126941); Mitoxantrone (PubMED CID: 4212); Nanoparticles; Neratinib (PubMED CID: 9915743); Novel chemotherapy; Olaparib (PubMED CID: 23725625); Paclitaxel (PubMED CID: 36314); Palbociclib (PubMED CID: 122706004); Pegylation; Pictilisib (PubMED CID: 17755052); Pilaralisib (PubMED CID: 56599306); Ribociclib (PubMED CID: 44631912); Rucaparib (PubMED CID: 9931954); Sonidegib (PubMED CID: 24775005); Sunitinib (PubMED CID: 5329102); Tamoxifen (PubMED CID: 2733526); Taselisib (PubMED CID: 51001932); Temozolomide (PubMED CID: 5394); Teniposide (PubMED CID: 452548); Topotecan (PubMED CID: 60700); Tucatinib (PubMED CID: 51039094); Veliparib (PubMED CID: 11960529); Vincristine (PubMED CID: 5978); Vinorelbine (PubMED CID: 5311497); Voxtalisib (PubMED CID: 49867926); Z-Endoxifen (PubMED CID: 10090750).
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2015: Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):31–42. - PubMed
-
- Rostami R, et al. Brain metastasis in breast cancer: a comprehensive literature review. J Neurooncol. 2016;127(3):407–14. - PubMed
-
- Serdy KM, et al. Male Breast Cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 2017;147(1):110–119. - PubMed
-
- Lassman AB, DeAngelis LM. Brain metastases. Neurol Clin. 2003;21(1):1–23. vii. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous