Selective inhibition of histamine-evoked Ca2+ signals by compartmentalized cAMP in human bronchial airway smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 29604964
- PMCID: PMC5893132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.12.002
Selective inhibition of histamine-evoked Ca2+ signals by compartmentalized cAMP in human bronchial airway smooth muscle cells
Abstract
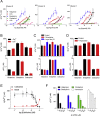
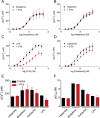
Intracellular Ca2+ and cAMP typically cause opposing effects on airway smooth muscle contraction. Receptors that stimulate these pathways are therapeutic targets in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. However, the interactions between different G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that evoke cAMP and Ca2+ signals in human bronchial airway smooth muscle cells (hBASMCs) are poorly understood. We measured Ca2+ signals in cultures of fluo-4-loaded hBASMCs alongside measurements of intracellular cAMP using mass spectrometry or [3H]-adenine labeling. Interactions between the signaling pathways were examined using selective ligands of GPCRs, and inhibitors of Ca2+ and cAMP signaling pathways. Histamine stimulated Ca2+ release through inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptors in hBASMCs. β2-adrenoceptors, through cAMP and protein kinase A (PKA), substantially inhibited histamine-evoked Ca2+ signals. Responses to other Ca2+-mobilizing stimuli were unaffected by cAMP (carbachol and bradykinin) or minimally affected (lysophosphatidic acid). Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), through EP2 and EP4 receptors, stimulated formation of cAMP and inhibited histamine-evoked Ca2+ signals. There was no consistent relationship between the inhibition of Ca2+ signals and the amounts of intracellular cAMP produced by different stimuli. We conclude that β-adrenoceptors, EP2 and EP4 receptors, through cAMP and PKA, selectively inhibit Ca2+ signals evoked by histamine in hBASMCs, suggesting that PKA inhibits an early step in H1 receptor signaling. Local delivery of cAMP within hyperactive signaling junctions mediates the inhibition.
Keywords: Airway smooth muscle; Ca(2+) signaling; Cyclic AMP; Histamine; Protein kinase A; Spatial organization.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2 Inhibits Histamine-Evoked Ca2+ Release in Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells through Hyperactive cAMP Signaling Junctions and Protein Kinase A.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;92(5):533-545. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.109249. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28877931 Free PMC article.
-
Ca(2+) signals evoked by histamine H1 receptors are attenuated by activation of prostaglandin EP2 and EP4 receptors in human aortic smooth muscle cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;169(7):1624-34. doi: 10.1111/bph.12239. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23638853 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of airway smooth muscle cell migration by E-prostanoid receptor subtypes.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Mar;48(3):322-9. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0158OC. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23221043
-
Regulation of IP3 receptors by cyclic AMP.Cell Calcium. 2017 May;63:48-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Nov 6. Cell Calcium. 2017. PMID: 27836216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cAMP and Ca²⁺ signaling in secretory epithelia: crosstalk and synergism.Cell Calcium. 2014 Jun;55(6):385-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Cell Calcium. 2014. PMID: 24613710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of TG2-Mediated SERCA2 Serotonylation on Hypoxic Pulmonary Vein Remodeling.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 11;10:1611. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01611. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32116663 Free PMC article.
-
Absinthin, an agonist of the bitter taste receptor hTAS2R46, uncovers an ER-to-mitochondria Ca2+-shuttling event.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 16;294(33):12472-12482. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007763. Epub 2019 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31248983 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine-induced cytosolic calcium mobilization in human bronchial smooth muscle cells.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2025;61:29-42. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.61.29. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2025. PMID: 40204453 Free PMC article.
-
The role of human mast cells in allergy and asthma.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7049-7064. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2044278. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35266441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle-matrix interactions.Nat Rev Mater. 2023 Jun;8(6):390-402. doi: 10.1038/s41578-023-00551-3. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Nat Rev Mater. 2023. PMID: 38463907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes P.J., Chung K.F., Page C.P. Inflammatory mediators of asthma: an update. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998;50:515–596. - PubMed
-
- Barnes P.J. Mediators of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004;56:515–548. - PubMed
-
- Bateman E.D., Hurd S.S., Barnes P.J., Bousquet J., Drazen J.M., FitzGerald M. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur. Respir. J. 2008;31:143–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

