PheWAS and Beyond: The Landscape of Associations with Medical Diagnoses and Clinical Measures across 38,662 Individuals from Geisinger
- PMID: 29606303
- PMCID: PMC5985339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.02.017
PheWAS and Beyond: The Landscape of Associations with Medical Diagnoses and Clinical Measures across 38,662 Individuals from Geisinger
Abstract
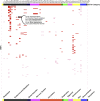
Most phenome-wide association studies (PheWASs) to date have used a small to moderate number of SNPs for association with phenotypic data. We performed a large-scale single-cohort PheWAS, using electronic health record (EHR)-derived case-control status for 541 diagnoses using International Classification of Disease version 9 (ICD-9) codes and 25 median clinical laboratory measures. We calculated associations between these diagnoses and traits with ∼630,000 common frequency SNPs with minor allele frequency > 0.01 for 38,662 individuals. In this landscape PheWAS, we explored results within diseases and traits, comparing results to those previously reported in genome-wide association studies (GWASs), as well as previously published PheWASs. We further leveraged the context of functional impact from protein-coding to regulatory regions, providing a deeper interpretation of these associations. The comprehensive nature of this PheWAS allows for novel hypothesis generation, the identification of phenotypes for further study for future phenotypic algorithm development, and identification of cross-phenotype associations.
Keywords: EHR; GWAS; PheWAS; bioinformatics; biorepository; genetic epidemiology; genomics; phenome-wide.
Copyright © 2018 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Hall M.A., Verma A., Brown-Gentry K.D., Goodloe R., Boston J., Wilson S., McClellan B., Sutcliffe C., Dilks H.H., Gillani N.B. Detection of pleiotropy through a phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) of epidemiologic data as part of the Environmental Architecture for Genes Linked to Environment (EAGLE) study. PLoS Genet. 2014;10:e1004678. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pendergrass S.A., Brown-Gentry K., Dudek S., Frase A., Torstenson E.S., Goodloe R., Ambite J.L., Avery C.L., Buyske S., Bůžková P. Phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) for detection of pleiotropy within the Population Architecture using Genomics and Epidemiology (PAGE) Network. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003087. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verma A., Basile A.O., Bradford Y., Kuivaniemi H., Tromp G., Carey D., Gerhard G.S., Crowe J.E., Jr., Ritchie M.D., Pendergrass S.A. Phenome-wide association study to explore relationships between immune system related genetic loci and complex traits and diseases. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0160573. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Namjou B., Marsolo K., Caroll R.J., Denny J.C., Ritchie M.D., Verma S.S., Lingren T., Porollo A., Cobb B.L., Perry C. Phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) in EMR-linked pediatric cohorts, genetically links PLCL1 to speech language development and IL5-IL13 to eosinophilic esophagitis. Front. Genet. 2014;5:401. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

