The reliability of lung ultrasound in assessment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 29606857
- PMCID: PMC5868611
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S156615
The reliability of lung ultrasound in assessment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
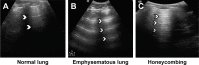
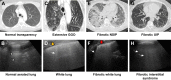
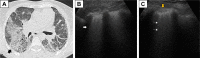
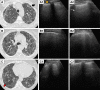
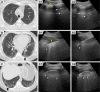
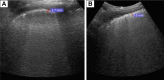
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the severest form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, with a median survival time estimated at 2-5 years from the time of diagnosis. It occurs mainly in elderly adults, suggesting a strong link between the fibrosis process and aging. Although chest high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is currently the method of choice in IPF assessment, diagnostic imaging with typical usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) provides definitive results in only 55%, requiring an invasive surgical procedure such as lung biopsy or cryobiopsy for the final diagnostic analysis. Lung ultrasound (LUS) as a noninvasive, non-radiating examination is very sensitive to detect subtle changes in the subpleural space. The evidence of diffuse, multiple B-lines defined as vertical, hyperechoic artifacts is the hallmark of interstitial syndrome. A thick, irregular, fragmented pleura line is associated with subpleural fibrotic scars. The total numbers of B-lines are correlated with the extension of pulmonary fibrosis on HRCT, being an LUS marker of severity. The average distance between two adjacent B-lines is an indicator of a particular pattern on HRCT. It is used to appreciate a pure reticular fibrotic pattern as in IPF compared with a predominant ground glass pattern seen in fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pattern. The distribution of the LUS artifacts has a diagnostic value. An upper predominance of multiple B-lines associated with the thickening of pleura line is an LUS feature of an inconsistent UIP pattern, excluding the IPF diagnosis. LUS is a repeatable, totally radiation-free procedure, well tolerated by patients, very sensitive in detecting early changes of fibrotic lung, and therefore a useful imaging technique in monitoring disease progression in the natural course or after initiation of treatment.
Keywords: B-lines artifacts; chest high-resolution computed tomography; chest ultrasound; interstitial lung diseases; interstitial syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Ultrasound mapping of lung changes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Clin Respir J. 2020 Jan;14(1):54-63. doi: 10.1111/crj.13101. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Clin Respir J. 2020. PMID: 31675455
-
Usual interstitial pneumonia end-stage features from explants with radiologic and pathological correlations.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015 Aug;19(4):269-76. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.05.003. Epub 2015 May 13. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26025258
-
Diagnosing fibrotic lung disease: when is high-resolution computed tomography sufficient to make a diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?Respirology. 2009 Sep;14(7):934-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2009.01626.x. Respirology. 2009. PMID: 19740255 Review.
-
Lung ultrasound for assessing disease progression in UIP and NSIP: a comparative study with HRCT and PFT/DLCO.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jan 9;25(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03433-8. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 39789530 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.J Thorac Imaging. 2016 May;31(3):127-39. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0000000000000204. J Thorac Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27043425 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between Transthoracic Lung Ultrasound Score and HRCT Features in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases.J Clin Med. 2019 Aug 11;8(8):1199. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081199. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31405211 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning diagnostic and severity-stratification for interstitial lung diseases and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in digital lung auscultations and ultrasonography: clinical protocol for an observational case-control study.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Jun 2;23(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02255-w. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37264374 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in Children: An Ample Review.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020 Jun 25;13:661-669. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S257180. eCollection 2020. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020. PMID: 32636686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Ultrasound Is More Sensitive for Hospitalized Consolidated Pneumonia Diagnosis Compared to CXR in Children.Children (Basel). 2021 Jul 29;8(8):659. doi: 10.3390/children8080659. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34438550 Free PMC article.
-
Laryngeal and pleural ultrasound and acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in dogs with brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 6;15(1):19884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94644-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40481134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King TE, Jr, Pardo A, Selman M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2011;378(9807):1949–1961. - PubMed
-
- Collard HR, King TE, Bartelson BB, Vourlekis JS, Schwarz MI, Brown KK. Changes in clinical and physiologic variables predict survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168(5):538–542. - PubMed
-
- Latsi PI, du Bois RM, Nicholson AG, et al. Fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: the prognostic value of longitudinal functional trends. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168(5):531–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

