The ultrastructure of subgingival dental plaque, revealed by high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscopy
- PMID: 29607057
- PMCID: PMC5842838
- DOI: 10.1038/bdjopen.2015.3
The ultrastructure of subgingival dental plaque, revealed by high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscopy
Abstract
Objectives/aims: To explore the ultrastructure of subgingival dental plaque using high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and to investigate whether extracellular DNA (eDNA) could be visualised in ex vivo samples.
Materials and methods: Ten patients were recruited who fulfilled the inclusion criteria (teeth requiring extraction with radiographic horizontal bone loss of over 50% and grade II/III mobility). In total, 12 teeth were extracted using a minimally traumatic technique. Roots were sectioned using a dental air turbine handpiece, under water cooling to produce 21 samples. Standard fixation and dehydration protocols were followed. For some samples, gold-labelled anti-DNA antibodies were applied before visualising biofilms by FE-SEM.
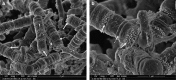
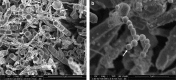
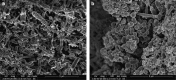
Results: High-resolution FE-SEMs of subgingival biofilm were obtained in 90% of the samples. The sectioning technique left dental plaque biofilms undisturbed. Copious amounts of extracellular material were observed in the plaque, which may have been eDNA as they had a similar appearance to labelled eDNA from in vitro studies. There was also evidence of membrane vesicles and open-ended tubular structures. Efforts to label eDNA with immune-gold antibodies were unsuccessful and eDNA was not clearly labelled.
Conclusions: High-resolution FE-SEM images were obtained of undisturbed subgingival ex vivo dental plaque biofilms. Important structural features were observed including extracellular polymeric material, vesicles and unusual open tubule structures that may be remnants of lysed cells. The application of an eDNA immune-gold-labelling technique, previously used successfully in in vitro samples, did not clearly identify eDNA in ex vivo samples. Further studies are needed to characterise the molecular composition of the observed extracellular matrix material.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Understanding the Matrix: The Role of Extracellular DNA in Oral Biofilms.Front Oral Health. 2021 Mar 22;2:640129. doi: 10.3389/froh.2021.640129. eCollection 2021. Front Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 35047995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Role for Extracellular DNA in Dental Plaque Formation.J Dent Res. 2017 Feb;96(2):208-216. doi: 10.1177/0022034516675849. Epub 2016 Oct 23. J Dent Res. 2017. PMID: 27770039
-
Enterococcus faecalis produces abundant extracellular structures containing DNA in the absence of cell lysis during early biofilm formation.mBio. 2012 Jul 24;3(4):e00193-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00193-12. Print 2012. mBio. 2012. PMID: 22829679 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilms: What does subgingival plaque look like?Br Dent J. 2016 Jul 8;221(1):16. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2016.487. Br Dent J. 2016. PMID: 27388079
-
Dental calculus: recent insights into occurrence, formation, prevention, removal and oral health effects of supragingival and subgingival deposits.Eur J Oral Sci. 1997 Oct;105(5 Pt 2):508-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1997.tb00238.x. Eur J Oral Sci. 1997. PMID: 9395117 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibodies with specificity to glycan motifs that decorate OMV cargo proteins.mSphere. 2025 Mar 25;10(3):e0090724. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00907-24. Epub 2025 Feb 26. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 40008882 Free PMC article.
-
The dental plaque biofilm matrix.Periodontol 2000. 2021 Jun;86(1):32-56. doi: 10.1111/prd.12361. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Periodontol 2000. 2021. PMID: 33690911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ever-changing landscape in modern dentistry therapeutics - Enhancing the emptying quiver of the periodontist.Heliyon. 2021 Nov 10;7(11):e08342. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08342. eCollection 2021 Nov. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34816039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benzyldimethyldodecyl Ammonium Chloride-Doped Denture-Based Resin: Impact on Strength, Surface Properties, Antifungal Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Analysis.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Oct 18;15(10):310. doi: 10.3390/jfb15100310. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39452608 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Matrix: The Role of Extracellular DNA in Oral Biofilms.Front Oral Health. 2021 Mar 22;2:640129. doi: 10.3389/froh.2021.640129. eCollection 2021. Front Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 35047995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gilbert P, Maira-Litran T, McBain AJ, Rickard AH, Whyte FW. The physiology and collective recalcitrance of microbial biofilm communities. Adv Microb Physiol 2002; 46: 202–256. - PubMed
-
- Moore WE, Moore LV. The bacteria of periodontal diseases. Periodontol. 2000 1994; 5: 66–77. - PubMed
-
- Pretty IA, Edgar WM, Smith PW, Higham SM. Quantification of dental plaque in the research environment. J Dent 2005; 33: 193–207. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

