Decreased expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) in a chronic intermittent hypoxia mouse model
- PMID: 29607154
- PMCID: PMC5864663
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.12.106
Decreased expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) in a chronic intermittent hypoxia mouse model
Erratum in
-
Erratum to decreased expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) in a chronic intermittent hypoxia mouse model.J Thorac Dis. 2020 May;12(5):2990. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.04.19. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32642214 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms, CYP1A2, is one of important enzymes for many drugs metabolism. Studies have confirmed that sustained hypoxia can influence the expression of hepatic CYP, including CYP1A2. The impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH), a marked characteristic of sleep apnea, on CYP1A2 remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of CIH on the expression of hepatic CYP1A2 in a mouse model with sleep apnea.
Methods: Twenty four old male (6-8 weeks) C57BL/6J mice (n=12 in each group) were randomly assigned to either normoxia group or CIH group. Mice in CIH group underwent 12 weeks intermittent hypoxia exposure. The different gene expression of hepatic CYP1A2 between two groups was analyzed by quantity real-time polymerase chain reaction. The protein levels of hepatic CYP1A2 in each group were observed by using western blotting and immunohistochemistry.
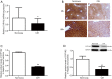
Results: After 12 weeks of exposure to intermittent hypoxia, the expression of hepatic CYP1A2, at the mRNA and protein levels was decreased more significantly in the CIH group than the normoxia group (P<0.01).
Conclusions: CIH contributes to inhibiting the expression of hepatic CYP1A2. This implies that the dosage of drugs metabolized by CYP1A2, should be adjusted in patients with sleep apnea.
Keywords: Intermittent hypoxia; cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2); drug metabolism; hepatic cytochrome P450 (hepatic CYP); sleep apnea.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Intermittent Hypoxia Inhibits Hepatic CYP1a2 Expression and Delays Aminophylline Metabolism.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 29;2022:2782702. doi: 10.1155/2022/2782702. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35529917 Free PMC article.
-
Angiopoietin-like proteins 8 knockout reduces intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular remodeling in a murine model of obstructive sleep apnea.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;186:114502. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114502. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33684391
-
Effect of chronic intermittent hypoxia on theophylline metabolism in mouse liver.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013 Jan;126(1):118-23. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013. PMID: 23286489
-
Metabolism and Mechanism of Human Cytochrome P450 Enzyme 1A2.Curr Drug Metab. 2021;22(1):40-49. doi: 10.2174/1389200221999210101233135. Curr Drug Metab. 2021. PMID: 33397254 Review.
-
Effect of chronic intermittent hypoxia on gene expression profiles of rat liver: a better understanding of OSA-related liver disease.Sleep Breath. 2020 Jun;24(2):761-770. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01987-0. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Sleep Breath. 2020. PMID: 31845084 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of a hypoxia-immune-related microenvironment gene signature and prediction model for hepatitis C-induced early-stage fibrosis.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 29;22(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04912-6. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38287425 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum to decreased expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) in a chronic intermittent hypoxia mouse model.J Thorac Dis. 2020 May;12(5):2990. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.04.19. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32642214 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Attenuates Tumor Oxidative Stress and Promotes Apoptosis in an Intermittent Hypoxia Mouse Model.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820928073. doi: 10.1177/1533033820928073. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32431212 Free PMC article.
-
Biological roles of cytochrome P450 1A1, 1A2, and 1B1 enzymes.Arch Pharm Res. 2021 Jan;44(1):63-83. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01306-w. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Arch Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 33484438 Review.
-
High-altitude Hypoxia Influences the Activities of the Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme CYP3A1 and the Pharmacokinetics of Four Cardiovascular System Drugs.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;15(10):1303. doi: 10.3390/ph15101303. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297415 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
