Comparison of survival between lung cancer patients receiving single or multiple-incision thoracoscopic surgery
- PMID: 29607166
- PMCID: PMC5864624
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2018.01.58
Comparison of survival between lung cancer patients receiving single or multiple-incision thoracoscopic surgery
Abstract
Background: The effect of single-incision thoracoscopic surgery for lung cancer on long-term survival is unknown and no studies have investigated whether there are differences in survival between single and multiple incision approaches. We aimed to compare long-term overall survival and disease-free survival of patients who underwent single-incision thoracoscopic surgery with those who received multiple-incision thoracoscopic surgery for lung cancer.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 532 patients with lung cancer who underwent either single-incision (n=150) or multiple-incision thoracoscopic resection (n=382) during the period January 2000 to December 2014. Patients were matched on propensity score at a 1:2 ratio to estimate the effect of treatment on long-term and disease-free survival. Overall survival and disease-free survival were assessed using the Kaplan-Meier method, the log-rank test and Cox proportional-hazards regression.
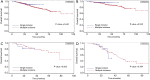
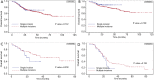
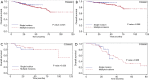
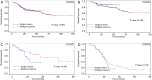
Results: Propensity matching resulted in 138 patients in the single-incision group and 276 patients in the multiple-incision group. The matched patients in the single-incision group had a significantly better 5-year overall survival than those in the multiple-incision group (P=0.027). Disease-free survival was similar between the two groups before and after matching. The number of chest wall incisions did not influence overall survival or disease-free survival.
Conclusions: The long-term outcomes of single-incision thoracoscopic surgery are comparable to those of multiple-incision thoracoscopic surgery for lung cancer.
Keywords: Survival; lung cancer; multiple-incision; single-incision; thoracoscopic surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Wang BY, Huang JY, Lin CH, et al. Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Produces Long-Term Survival Similar to That with Open Lobectomy in Cases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Propensity-Matched Analysis Using a Population-Based Cancer Registry. J Thorac Oncol 2016;11:1326-34. 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.04.032 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
