Nutritional Ketosis and Mitohormesis: Potential Implications for Mitochondrial Function and Human Health
- PMID: 29607218
- PMCID: PMC5828461
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/5157645
Nutritional Ketosis and Mitohormesis: Potential Implications for Mitochondrial Function and Human Health
Abstract
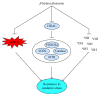
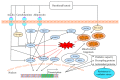
Impaired mitochondrial function often results in excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and is involved in the etiology of many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. Moderate levels of mitochondrial ROS, however, can protect against chronic disease by inducing upregulation of mitochondrial capacity and endogenous antioxidant defense. This phenomenon, referred to as mitohormesis, is induced through increased reliance on mitochondrial respiration, which can occur through diet or exercise. Nutritional ketosis is a safe and physiological metabolic state induced through a ketogenic diet low in carbohydrate and moderate in protein. Such a diet increases reliance on mitochondrial respiration and may, therefore, induce mitohormesis. Furthermore, the ketone β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), which is elevated during nutritional ketosis to levels no greater than those resulting from fasting, acts as a signaling molecule in addition to its traditionally known role as an energy substrate. BHB signaling induces adaptations similar to mitohormesis, thereby expanding the potential benefit of nutritional ketosis beyond carbohydrate restriction. This review describes the evidence supporting enhancement of mitochondrial function and endogenous antioxidant defense in response to nutritional ketosis, as well as the potential mechanisms leading to these adaptations.
Figures
References
-
- Tapia P. C. Sublethal mitochondrial stress with an attendant stoichiometric augmentation of reactive oxygen species may precipitate many of the beneficial alterations in cellular physiology produced by caloric restriction, intermittent fasting, exercise and dietary phytonutrients: “Mitohormesis” for health and vitality. Medical Hypotheses. 2006;66(4):832–843. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2005.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

