Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Mediates the Protective Effect of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor on Renal Fibrosis via Reducing the Phenotypic Conversion of Renal Microvascular Cells in Monocrotaline-Treated Rats
- PMID: 29607314
- PMCID: PMC5828432
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1864107
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Mediates the Protective Effect of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor on Renal Fibrosis via Reducing the Phenotypic Conversion of Renal Microvascular Cells in Monocrotaline-Treated Rats
Abstract
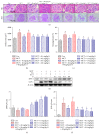
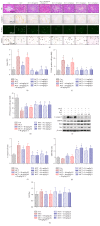
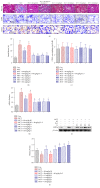
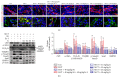
Chronic kidney diseases are characterized by renal fibrosis with excessive matrix deposition, leading to a progressive loss of functional renal parenchyma and, eventually, renal failure. Renal microcirculation lesions, including the phenotypic conversion of vascular cells, contribute to renal fibrosis. Here, renal microcirculation lesions were established with monocrotaline (MCT, 60 mg/kg). Sitagliptin (40 mg/kg/d), a classical dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, attenuated the renal microcirculation lesions by inhibiting glomerular tuft hypertrophy, glomerular mesangial expansion, and microvascular thrombosis. These effects of sitagliptin were mediated by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), since they were blocked by the GLP-1R antagonist exendin-3 (Ex-3, 40 ug/kg/d). The GLP-1R agonist liraglutide showed a similar renal protective effect in a dose-independent manner. In addition, sitagliptin, as well as liraglutide, alleviated the MCT-induced apoptosis of renal cells by increasing the expression of survival factor glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), which was abolished by the GLP-1R antagonist Ex-3. Sitagliptin and liraglutide also effectively ameliorated the conversion of vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from a synthetic phenotype to contractile phenotype. Moreover, sitagliptin and liraglutide inhibited endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) via downregulating transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1). Collectively, these findings suggest that DPP-4 inhibition can reduce microcirculation lesion-induced renal fibrosis in a GLP-1-dependent manner.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) mediates the protective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition on pulmonary hypertension.J Biomed Sci. 2019 Jan 12;26(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0496-y. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 30634956 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitor Sitagliptin on Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases 1/2 Signaling in Rats with Diabetic Nephropathy.Pharmacology. 2017;100(1-2):1-13. doi: 10.1159/000455874. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Pharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28329747
-
Weight Loss-Independent Effect of Liraglutide on Insulin Sensitivity in Individuals With Obesity and Prediabetes.Diabetes. 2024 Jan 1;73(1):38-50. doi: 10.2337/db23-0356. Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 37874653 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiovascular Actions and Clinical Outcomes With Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors.Circulation. 2017 Aug 29;136(9):849-870. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028136. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28847797 Review.
-
Intestinal regulation of urinary sodium excretion and the pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease: a focus on glucagon-like peptide 1 and dipeptidyl peptidase 4.Exp Physiol. 2014 Sep;99(9):1140-5. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2014.078766. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Exp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25085841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rodent Models of Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure for Translational Investigations and Therapeutic Discovery.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3162. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043162. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting cyclin-dependent kinases for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun. 2019 May 17;10(1):2204. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10135-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31101827 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition: Role in Physiology and in the Pathogenesis of Human Diseases.Physiol Rev. 2019 Apr 1;99(2):1281-1324. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2018. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30864875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oral Delivery System of Modified GLP-1 by Probiotics for T2DM.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 10;15(4):1202. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041202. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111687 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: Focus on Endothelial Dysfunctions and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 7;12(8):1795. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081795. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

