Estimated Prevalence of Adolescents with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korea
- PMID: 29607635
- PMCID: PMC5879040
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e109
Estimated Prevalence of Adolescents with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korea
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become prevalent worldwide in the last decade. However, the recent prevalence of NAFLD in adolescents has not yet been investigated in Korea.
Methods: Data were obtained from 1,416 participants aged 10-18 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted in 2010 and 2015. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), height, weight, waist circumference (WC), body mass index (BMI), fasting glucose, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level, waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), and pediatric NAFLD fibrosis index (PNFI) were analyzed.
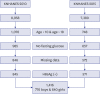
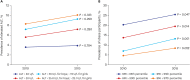
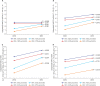
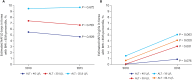
Results: SBP, weight, WC, BMI, WHtR, and total cholesterol level were significantly higher in 2015 than in 2010. Prevalence of NAFLD (BMI ≥ 85th percentile plus ALT > 30 U/L for boys and ALT > 19 U/L for girls) were 4.7% in 2010 and 5.9% in 2015 (P = 0.360). Using various cutoffs for the ALT level (> 40, > 30, > 25.8 U/L for boys and >22.1 U/L for girls) NAFLD prevalence rates were 3.0%, 4.1%, and 5.5% in 2010; 2.9%, 5.0%, and 7.1% in 2015, respectively (P = 0.899, 0.469, and 0.289). Boys had a higher SBP, DBP, height, weight, WC, BMI, WHtR, fasting glucose, total cholesterol, ALT, and lower HDL level than girls. The probability of liver fibrosis using the PNFI varies between 21.3% and 24.5% among NAFLD participants (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The Korean society needs to quickly control the increasing prevalence of NAFLD in adolescents and reduce its complications.
Keywords: Adolescents; Estimated; Korea; Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; Prevalence.
© 2018 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Suchy FJ, Sokol RJ, Balistreri WF. Liver Disease in Children. 4th ed. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 2014.
-
- Matteoni CA, Younossi ZM, Gramlich T, Boparai N, Liu YC, McCullough AJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology. 1999;116(6):1413–1419. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129(1):113–121. - PubMed
-
- Das K, Das K, Mukherjee PS, Ghosh A, Ghosh S, Mridha AR, et al. Nonobese population in a developing country has a high prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver and significant liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51(5):1593–1602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

