Hedgehog signaling contributes to bone cancer pain by regulating sensory neuron excitability in rats
- PMID: 29607715
- PMCID: PMC5888817
- DOI: 10.1177/1744806918767560
Hedgehog signaling contributes to bone cancer pain by regulating sensory neuron excitability in rats
Abstract
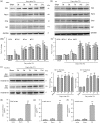
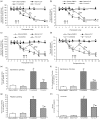
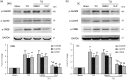
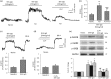
Treating bone cancer pain continues to be a clinical challenge and underlying mechanisms of bone cancer pain remain elusive. Here, we reported that sonic hedgehog signaling plays a critical role in the development of bone cancer pain. Tibia bone cavity tumor cell implantation produces bone cancer-related mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia, and spontaneous and movement-evoked pain behaviors. Production and persistence of these pain behaviors are well correlated with tumor cell implantation-induced up-regulation and activation of sonic hedgehog signaling in primary sensory neurons and spinal cord. Spinal administration of sonic hedgehog signaling inhibitor cyclopamine prevents and reverses the induction and persistence of bone cancer pain without affecting normal pain sensitivity. Inhibiting sonic hedgehog signaling activation with cyclopamine, in vivo or in vitro, greatly suppresses tumor cell implantation-induced increase of intracellular Ca2+ and hyperexcitability of the sensory neurons and also the activation of GluN2B receptor and the subsequent Ca2+-dependent signals CaMKII and CREB in dorsal root ganglion and the spinal cord. These findings show a critical mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of bone cancer pain and suggest that targeting sonic hedgehog signaling may be an effective approach for treating bone cancer pain.
Keywords: Sonic hedgehog; bone cancer pain; dorsal root ganglion; excitability; neuron.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wnt/Ryk signaling contributes to neuropathic pain by regulating sensory neuron excitability and spinal synaptic plasticity in rats.Pain. 2015 Dec;156(12):2572-2584. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000366. Pain. 2015. PMID: 26407042
-
Blocking EphB1 receptor forward signaling in spinal cord relieves bone cancer pain and rescues analgesic effect of morphine treatment in rodents.Cancer Res. 2011 Jul 1;71(13):4392-402. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3870. Epub 2011 May 9. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21555368
-
Wnt5a/Ryk signaling contributes to bone cancer pain by sensitizing the peripheral nociceptors through JNK-mediated TRPV1 pathway in rats.Pain. 2025 Mar 1;166(3):680-692. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003426. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Pain. 2025. PMID: 39382316
-
Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway: A Role in Pain Processing.Neurochem Res. 2023 Jun;48(6):1611-1630. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03864-5. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36738366 Review.
-
Peripheral Mechanism of Cancer-Induced Bone Pain.Neurosci Bull. 2024 Jun;40(6):815-830. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01126-6. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Neurosci Bull. 2024. PMID: 37798428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analgesia of percutaneous thermal ablation plus cementoplasty for cancer bone metastases.J Bone Oncol. 2019 Nov 5;19:100266. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2019.100266. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Bone Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31788416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The insulin receptor regulates the persistence of mechanical nociceptive sensitization in flies and mice.Biol Open. 2023 Jun 15;12(6):bio059864. doi: 10.1242/bio.059864. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Biol Open. 2023. PMID: 37259940 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Stimulation Alleviates CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain Via Suppressing P2X3 Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 2;20(13):3248. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133248. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31269659 Free PMC article.
-
The Primary Cilium and its Hedgehog Signaling in Nociceptors Contribute to Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 26:rs.3.rs-3812442. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3812442/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 38464172 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Distinct Gene Expression Patterns of Ion Channels and Cytokines in Rat Primary Sensory Neurons During Development of Bone Cancer and Cancer Pain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 May 6;14:665085. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.665085. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34025351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van den Beuken-van Everdingen MH, de Rijke JM, Kessels AG.Schouten HC, van Kleef M, Patinjn J. Prevalence of pain in patients with cancer: a systematic review of the past 40 years. Ann Oncol 2007; 18: 1437–1449. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Liu W, Liu YP.Dong HL, Henkemeyer M, Xiong LZ, Song XJ. Blocking EphB1 receptor forward signaling in spinal cord relieves bone cancer pain and rescues analgesic effect of morphine treatment in rodents. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 4392–4402. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Liu YP, Huang ZJ.Zhang YK, Song AA, Ma PC, Song XJ. Wnt/Ryk signaling contributes to neuropathic pain by regulating sensory neuron excitability and spinal synaptic plasticity in rats. Pain 2015; 156: 2572–2584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

