Clinical Characteristics, Phenotype of Lipodystrophy and a Genetic Analysis of Six Diabetic Japanese Women with Familial Partial Lipodystrophy in a Diabetic Outpatient Clinic
- PMID: 29607946
- PMCID: PMC6148158
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0225-17
Clinical Characteristics, Phenotype of Lipodystrophy and a Genetic Analysis of Six Diabetic Japanese Women with Familial Partial Lipodystrophy in a Diabetic Outpatient Clinic
Abstract
Objective Our aim was to examine the clinical characteristics and phenotype of lipodystrophy of six diabetic Japanese women with partial lipodystrophy (PL) who received a genetic analysis at a diabetic outpatient clinic. Methods We screened for PL using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) among patients who had a reduced peripheral skinfold thickness at the diabetic outpatient clinic of Kusatsu General Hospital between August 2003 and August 2013. We performed a mutation analysis of candidate genes, including LMNA and PPARG, in two patients with PL and whole-exome sequencing in four patients with PL. Results We identified 15 patients with PL and performed a genetic analysis in 6 of them. They had no mutations in candidate genes known to be associated with familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD). They all had near-complete loss of subcutaneous fat, particularly in the antero-lateral and posterior thigh region and the calf region. As almost all patients were characterized by fat loss in the lower limbs with abdominal fat accumulation, a high rate of positivity for a family history, diabetes, and an unknown genetic cause, we suspected they might have FPLD1. Some patients have shown relatively severe insulin resistance, while others have shown insulin deficiency. Four and one had severe atherosclerosis and liver cirrhosis, probably due to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, respectively. Conclusion Almost all patients with PL identified in a diabetic outpatient clinic had subcutaneous fat loss in the lower limbs with excess truncal fat and might have had FPLD1.
Keywords: diabetic outpatient clinic; familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD); partial lipodystrophy (PL).
Figures
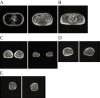
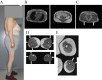
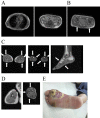
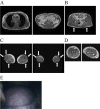
Similar articles
-
Clinical presentations, metabolic abnormalities and end-organ complications in patients with familial partial lipodystrophy.Metabolism. 2017 Jul;72:109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.04.010. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Metabolism. 2017. PMID: 28641778
-
Familial partial lipodystrophy linked to a novel peroxisome proliferator activator receptor -γ (PPARG) mutation, H449L: a comparison of people with this mutation and those with classic codon 482 Lamin A/C (LMNA) mutations.Diabet Med. 2016 Oct;33(10):1445-50. doi: 10.1111/dme.13061. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Diabet Med. 2016. PMID: 26756202
-
Diagnostic Value of Anthropometric Measurements for Familial Partial Lipodystrophy, Dunnigan Variety.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jul 1;105(7):2132-41. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa137. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32193531 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Management of Genetic Lipodystrophy Syndromes and its Implications for Atherosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025 May 13;27(1):55. doi: 10.1007/s11883-025-01301-2. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025. PMID: 40358796 Review.
-
Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Sisters with LMNA Associated Familial Partial Lipodystrophy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2020 Dec;129(12):1243-1246. doi: 10.1177/0003489420933645. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2020. PMID: 32517491 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic and Genetic Characteristics of Lipodystrophy: Pathophysiology, Metabolic Abnormalities, and Comorbidities.Curr Diab Rep. 2018 Nov 8;18(12):143. doi: 10.1007/s11892-018-1099-9. Curr Diab Rep. 2018. PMID: 30406415 Review.
-
Observation of p.R4810K, a Polymorphism of the Mysterin Gene, the Susceptibility Gene for Moyamoya Disease, in Two Female Japanese Diabetic Patients with Familial Partial Lipodystrophy 1.Intern Med. 2020;59(20):2529-2537. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4042-19. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 33055470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal AK, Garg A. Genetic basis of lipodystrophies and management of metabolic complications. Annu Rev Med 57: 297-311, 2006. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

