The SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Significantly Improves the Peripheral Microvascular Endothelial Function in Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 29607968
- PMCID: PMC6120841
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0701-17
The SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Significantly Improves the Peripheral Microvascular Endothelial Function in Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
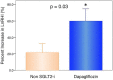
Objective Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors reduce cardiovascular events and decrease the body fat mass in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We examined whether or not the SGLT2-inhibitor dapagliflozin can improve the endothelial function associated with a reduction in abdominal fat mass. Methods We prospectively recruited patients with uncontrolled [hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) >7.0%] T2DM who were not being treated by SGLT2 inhibitors. Patients were treated with add-on dapagliflozin (5 mg/day) or non-SGLT2 inhibitor medicines for 6 months to improve their HbA1c. We measured the peripheral microvascular endothelial function as assessed by reactive hyperemia peripheral arterial tonometry (RH-PAT) and calculated the natural logarithmic transformed value of the RH-PAT index (LnRHI). We then investigated changes in the LnRHI and abdominal fat area using computed tomography (CT). Results The subjects were 54 patients with uncontrolled T2DM (72.2% men) with a mean HbA1c of 8.1%. The HbA1c was significantly decreased in both groups, with no significant difference between the groups. Dapagliflozin treatment, but not non-SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, significantly increased the LnRHI. The changes in the LnRHI were significantly greater in the dapagliflozin group than in the non-SGLT2 inhibitor group. Dapagliflozin treatment, but not non-SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, significantly decreased the abdominal visceral fat area, subcutaneous fat area (SFA), and total fat area (TFA) as assessed by CT and significantly increased the plasma adiponectin levels. The percentage changes in the LnRHI were significantly correlated with changes in the SFA, TFA, systolic blood pressure, and adiponectin. Conclusion Add-on treatment with dapagliflozin significantly improves the glycemic control and endothelial function associated with a reduction in the abdominal fat mass in patients with uncontrolled T2DM.
Keywords: endothelial function; fat mass; sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor; type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dapagliflozin significantly reduced liver fat accumulation associated with a decrease in abdominal subcutaneous fat in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018 Aug;142:254-263. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 May 31. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018. PMID: 29859912
-
Effectiveness of dapagliflozin on vascular endothelial function and glycemic control in patients with early-stage type 2 diabetes mellitus: DEFENCE study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Jul 6;16(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0564-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28683796 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, in diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 Oct 17;14:142. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0297-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 26474563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of intermittent use of the SGLT-2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes in Japan: a randomized, crossover, controlled clinical trial.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;18(8):743-751. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2017.1317748. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28426260 Clinical Trial.
-
[Dapagliflozin, the first SGLT-2 inhibitor in the treatment of type 2 diabetes].Med Clin (Barc). 2013 Sep;141 Suppl 2:36-43. doi: 10.1016/S0025-7753(13)70062-9. Med Clin (Barc). 2013. PMID: 24444523 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Effects of SGLT-2 Inhibitors on Vascular Endothelial Function and Arterial Stiffness in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 16;13:826604. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.826604. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35250882 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective Effects of Additional SGLT2 inhibitor Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3b-4: A Real World Report From A Japanese Specialized Diabetes Care Center.J Clin Med Res. 2019 Apr;11(4):267-274. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3761. Epub 2019 Mar 18. J Clin Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30937117 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Cardiovascular and Lower Limb Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Mar 28;18:917-929. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S515384. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40171412 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Therapeutics for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-A Look at the Past Decade and a Glimpse into the Future.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 21;12(7):1386. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071386. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors on Vascular Cell Function and Arterial Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 16;22(16):8786. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168786. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vallon V. The mechanisms and therapeutic potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Med 66: 255-270, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Bolinder J, Ljunggren O, Kullberg J, et al. . Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97: 1020-1031, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Ribola FA, Cancado FB, Schoueri JH, De Toni VF, Medeiros VH, Feder D. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21: 199-211, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Scheen AJ, Van Gaal LF. Combating the dual burden: therapeutic targeting of common pathways in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2: 911-922, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Tahrani AA, Barnett AH, Bailey CJ. Pharmacology and therapeutic implications of current drugs for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12: 566-592, 2016. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

