Homo sapiens-Specific Binding Site Variants within Brain Exclusive Enhancers Are Subject to Accelerated Divergence across Human Population
- PMID: 29608725
- PMCID: PMC5952923
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evy052
Homo sapiens-Specific Binding Site Variants within Brain Exclusive Enhancers Are Subject to Accelerated Divergence across Human Population
Abstract
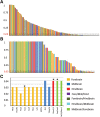
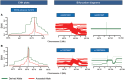
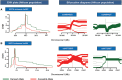
Empirical assessments of human accelerated noncoding DNA frgaments have delineated presence of many cis-regulatory elements. Enhancers make up an important category of such accelerated cis-regulatory elements that efficiently control the spatiotemporal expression of many developmental genes. Establishing plausible reasons for accelerated enhancer sequence divergence in Homo sapiens has been termed significant in various previously published studies. This acceleration by including closely related primates and archaic human data has the potential to open up evolutionary avenues for deducing present-day brain structure. This study relied on empirically confirmed brain exclusive enhancers to avoid any misjudgments about their regulatory status and categorized among them a subset of enhancers with an exceptionally accelerated rate of lineage specific divergence in humans. In this assorted set, 13 distinct transcription factor binding sites were located that possessed unique existence in humans. Three of 13 such sites belonging to transcription factors SOX2, RUNX1/3, and FOS/JUND possessed single nucleotide variants that made them unique to H. sapiens upon comparisons with Neandertal and Denisovan orthologous sequences. These variants modifying the binding sites in modern human lineage were further substantiated as single nucleotide polymorphisms via exploiting 1000 Genomes Project Phase3 data. Long range haplotype based tests laid out evidence of positive selection to be governing in African population on two of the modern human motif modifying alleles with strongest results for SOX2 binding site. In sum, our study acknowledges acceleration in noncoding regulatory landscape of the genome and highlights functional parts within it to have undergone accelerated divergence in present-day human population.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolutionary relevance of single nucleotide variants within the forebrain exclusive human accelerated enhancer regions.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Mar 29;24(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12860-023-00474-5. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36991330 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistically Distinct Pathways of Divergent Regulatory DNA Creation Contribute to Evolution of Human-Specific Genomic Regulatory Networks Driving Phenotypic Divergence of Homo sapiens.Genome Biol Evol. 2016 Sep 19;8(9):2774-88. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw185. Genome Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27503290 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable Elements and DNA Methylation Create in Embryonic Stem Cells Human-Specific Regulatory Sequences Associated with Distal Enhancers and Noncoding RNAs.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 May 7;7(6):1432-54. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv081. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25956794 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of cis-regulatory elements using binding site matrices--the successes, the failures and the reasons for both.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005 Aug;15(4):395-402. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.05.002. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005. PMID: 15950456 Review.
-
The Functionality and Evolution of Eukaryotic Transcriptional Enhancers.Adv Genet. 2016;96:143-206. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Adv Genet. 2016. PMID: 27968730 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Insights into Facial Variation and Craniofacial Development: Unraveling the Interplay of Genes, Expression Patterns, and Evolutionary Significance.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 26. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01349-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39724323
-
An Evolutionary Insight Into the Heterogeneous Severity Pattern of the SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 22;13:859508. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.859508. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35391792 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulation and the architecture of complex human traits in the genomics era.Curr Opin Psychol. 2019 Jun;27:93-97. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2019.02.011. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Curr Opin Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30933894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combinatorial binding syntax of transcription factors in forebrain-specific enhancers.Biol Open. 2025 Feb 15;14(2):BIO061751. doi: 10.1242/bio.061751. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Biol Open. 2025. PMID: 39976127 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Selection and Constraint on Human Knee Chondrocyte Regulation Impacts Osteoarthritis Risk.Cell. 2020 Apr 16;181(2):362-381.e28. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.057. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32220312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barreiro LB, Laval G, Quach H, Patin E, Quintana-Murci L.. 2008. Natural selection has driven population differentiation in modern humans. Nat Genet. 403:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Beccari L, Conte I, Cisneros E, Bovolenta P.. 2012. Sox2-mediated differential activation of Six3.2 contributes to forebrain patterning. Development 1391:151–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

