High frequency of M. leprae DNA detection in asymptomatic household contacts
- PMID: 29609530
- PMCID: PMC5879567
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3056-2
High frequency of M. leprae DNA detection in asymptomatic household contacts
Abstract
Background: Characterization of the Mycobacterium leprae genome has made possible the development of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) systems that can amplify different genomic regions. Increased reliability and technical efficiency of quantitative PCR (qPCR) makes it a promising tool for early diagnosis of leprosy. Index cases that are multibacillary spread the bacillus silently, even before they are clinically diagnosed. Early detection and treatment could prevent transmission in endemic areas.
Methods: In this study, the qPCR technique is used to detect DNA of M. leprae in samples of slit skin smears (SSS) of the ear lobe and blood of leprosy patients and their asymptomatic household contacts residing in Governador Valadares, MG, Brazil, a hyperendemic area for leprosy. A total of 164 subjects participated in the study: 43 index cases, 113 household contacts, and, as negative controls, 8 individuals who reported no contact with patients nor history of leprosy in the family. The qPCR was performed to amplify 16S rRNA fragments and was specifically designed for M. leprae.
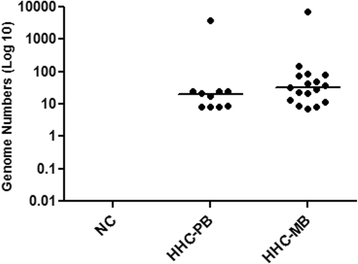
Results: Of asymptomatic household contacts, 23.89% showed bacillary DNA by qPCR in samples of SSS and blood. Also, 48.84% of patients diagnosed with leprosy were positive for qPCR while the bacillary load was positive in only 30.23% of patients. It is important to note that most patients were already receiving treatment when the collection of biological material for qPCR was performed. The level of bacillary DNA from household contacts was similar to the DNA levels detected in the group of paucibacillary patients.
Conclusion: Considering that household contacts comprise a recognizable group of individuals with a high risk of disease, as they live in close proximity to a source of infection, qPCR can be used to estimate the risk of progress towards leprosy among household contacts and as a routine screening method for a chemoprophylactic protocol.
Keywords: Household contacts; Leprosy; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
We hereby declare that this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Universidade Vale do Rio Doce—Univale, filed under N° PQ 022/09–009. All participants signed a free and informed consent at the first evaluation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Lyon S, Moura ACL, Grossi MAF, Silva RC. Dermatologia Tropical. 1a ed. Belo Horizonte: Medbook; 2016.
-
- WHO Global leprosy update, 2016: accelerating reduction of disease burden. Wkly Epid Rec. 2017;92:501–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

