Association of polymorphism rs1053005 in STAT3 with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Han Chinese population
- PMID: 29609539
- PMCID: PMC5879595
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-018-0569-x
Association of polymorphism rs1053005 in STAT3 with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Han Chinese population
Abstract
Background: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is involved in hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The association between polymorphism rs1053005 and haplotypes formed by rs1053004 and rs1053005 in the 3'UTR of STAT3 and chronic HBV infection has yet to be investigated.
Methods: This study included 567 patients with chronic HBV infection (239 chronic hepatitis, 141 liver cirrhosis and 187 HCC), 98 HBV infection resolvers, and 169 healthy controls. STAT3 rs1053004 and rs1053005 polymorphisms were genotyped by TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays.
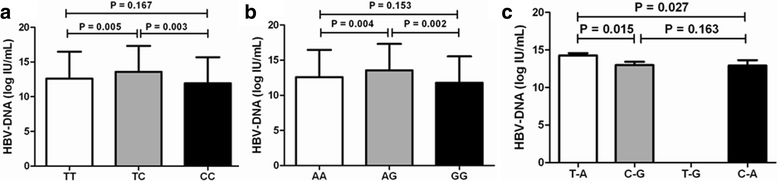
Results: The rs1053004 genotype CC [P value by Bonferroni correction (P c ) = 0.002] and allele C (P c = 0.019) were more frequent in patients with chronic HBV infection than in healthy controls. The rs1053005 genotype GG was also more frequent in patients with chronic HBV infection than in healthy controls (P c = 0.046). The rs1053004-rs1053005 haplotype T-G was less frequent in patients with chronic HBV infection than in healthy controls (Pc < 0.001). Haplotype C-A was more frequent in patients with liver cirrhosis than in patients with HCC (P c = 0.042). The rs1053004 genotype TC, rs1053005 genotype AG and rs1053004-rs1053005 haplotype T-A were associated with higher HBV DNA levels.
Conclusions: STAT3 rs1053004 and rs1053005 polymorphisms and haplotypes formed by rs1053004 and rs1053005 are associated with chronic HBV infection and the haplotypes appear to be also associated with the development of liver disease. Studies in large sample sizes of patients and control populations are required to verify and extend these findings.
Keywords: Clinical disease; Hepatitis B virus; STAT3; rs1053004; rs1053005.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University. All the participants provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Associations between gene polymorphisms of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and the susceptibility to hepatitis B virus related liver cirrhosis].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Feb 6;56(2):185-191. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20210818-00802. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35184448 Chinese.
-
Evaluation of STAT3 rs1053004 single nucleotide polymorphism in patients with chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017 Dec 30;63(12):45-50. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2017.63.12.11. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017. PMID: 29307341
-
Interleukin-21 gene polymorphisms and chronic hepatitis B infection in a Chinese population.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 14;21(14):4232-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4232. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25892873 Free PMC article.
-
Association of STAT3 and STAT4 polymorphisms with susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B virus infection and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jun 20;39(6):BSR20190783. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190783. Print 2019 Jun 28. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31160486 Free PMC article.
-
PNPLA3 rs738409 is not associated with the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and persistent infection of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in HBV-related subjects: A case-control study and meta-analysis on Asians.Gene. 2020 Jun 5;742:144585. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144585. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32173542
Cited by
-
Relation of STAT3 rs1053005 Variation and miR-452-3p with Osteoarthritis Susceptibility and Severity and the Clinical Response to High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid Injection in Osteoarthritis Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;13(23):3544. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13233544. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38066785 Free PMC article.
-
Association between STAT3 rs1053004 polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Mol Biol Res Commun. 2018 Sep;7(3):119-124. doi: 10.22099/mbrc.2018.29688.1323. Mol Biol Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30426029 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics and Functional Mechanisms of STAT3 Polymorphisms in Human Tuberculosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jul 7;11:669394. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.669394. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34307193 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Association between Inflammatory-Related Polymorphism in STAT3, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and Idiopathic Recurrent Implantation Failure.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 5;14(8):1588. doi: 10.3390/genes14081588. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628639 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 rs1053005 (T/C) contributes to Behçet's disease risk and ocular lesions.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Aug 14. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07628-0. Online ahead of print. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40813733
References
-
- Maini MK, Boni C, Lee CK, Larrubia JR, Reignat S, Ogg GS, King AS, Herberg J, Gilson R, Alisa A, et al. The role of virus-specific CD8(+) cells in liver damage and viral control during persistent hepatitis B virus infection. J Exp Med. 2000;191:1269–1280. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.8.1269. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous