CHRNA5 and CHRNA3 polymorphism and lung cancer susceptibility in Palestinian population
- PMID: 29609626
- PMCID: PMC5879790
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-018-3310-0
CHRNA5 and CHRNA3 polymorphism and lung cancer susceptibility in Palestinian population
Abstract
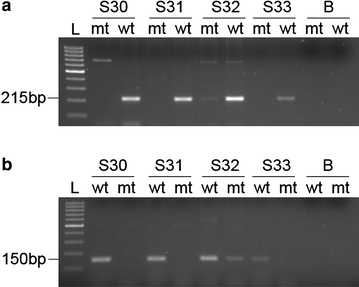
Objective: The genetic polymorphism (rs16969968 in CHRNA5, and rs1051730 in CHRNA3 genes) were recently shown to be associated with risk of LC. The aim of this study is to elucidate whether they predispose Palestinian individuals to lung cancer, and how is this related to smoking.
Results: Frequency of the rs16969968-A allele was significantly higher in the case group (36.7%) than in normal controls (17.5%; P = 0.022; OR = 6.83 for AA and 2.81 for AG genotypes). The frequency of rs1051730-T allele was also significantly higher in the case group (46.7%) than in the control group (22.5%; P = 0.001; OR = 2.20 for TC and 13.22 for TT genotypes). Frequency of rs16969968-A allele was higher in smokers (29.1%) than nonsmokers (15.7%) regardless of lung cancer; similarly, frequency of rs1051730-T allele was also higher in smokers than in smokers (46.7% vs 22.5%, respectively). The higher the proportion of the risk allele (rs16969968-A and rs1051730-T), the higher the mean number of daily consumed cigarettes (P = 0.006). Carrying rs16969968-A and/or rs1051730-T alleles results in an increased risk to lung cancer probably by increasing the individual's tendency for heavy smoking. The allelic frequency of the rs16969968-A and rs1051730-T alleles among normal Palestinian controls is similar to different populations worldwide.
Keywords: ASP-PCR; CHRNA3; CHRNA5; Gaza strip; Lung cancer; nAChR; rs1051730; s16969968.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CHRNA3 rs1051730 and CHRNA5 rs16969968 polymorphisms are associated with heavy smoking, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a mexican population.Ann Hum Genet. 2018 Nov;82(6):415-424. doi: 10.1111/ahg.12264. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Ann Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29993116
-
The relationship between CHRNA5/A3/B4 gene cluster polymorphisms and lung cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis and systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Feb 12;100(6):e24355. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024355. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33578531 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Polymorphism CHRNA5 and CHRNA3 Gene in People Addicted to Nicotine.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 23;19(17):10478. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710478. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36078193 Free PMC article.
-
Association between genetic variants on chromosome 15q25 locus and objective measures of tobacco exposure.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 May 16;104(10):740-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs191. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 22534784 Free PMC article.
-
CHRNA5 rs16969968 polymorphism is associated with lung cancer risk: A meta-analysis.Clin Respir J. 2020 Jun;14(6):505-513. doi: 10.1111/crj.13165. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Clin Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32049419 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of TERT, OGG1, and CHRNA5 Polymorphisms and the Predisposition to Lung Cancer in Eastern Algeria.Pulm Med. 2020 Mar 20;2020:7649038. doi: 10.1155/2020/7649038. eCollection 2020. Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 32257438 Free PMC article.
-
Gene signature to predict prognostic survival of hepatocellular carcinoma.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Jan 7;17(1):135-150. doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0405. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. PMID: 35071775 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking-Related Increases in Alcohol Outcomes and Preliminary Evidence for the Protective Effect of a Functional Nicotine Receptor Gene (CHRNA5) Variant on Alcohol Consumption in Individuals Without Alcohol Use Disorder.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024 Oct 1;27(10):pyae035. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyae035. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39208422 Free PMC article.
-
The CHRNA5 Polymorphism (rs16969968) and its Association with Waterpipe Smoking Addiction among Jordanians.Arab J Basic Appl Sci. 2020;27(1):450-455. doi: 10.1080/25765299.2020.1849491. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Arab J Basic Appl Sci. 2020. PMID: 33511332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ervik M, Lam F, Ferlay J, Mery L, Soerjomataram I, Bray F. Cancer fact sheets: lung cancer. 2016. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

