Solar geoengineering as part of an overall strategy for meeting the 1.5°C Paris target
- PMID: 29610384
- PMCID: PMC5897825
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2016.0454
Solar geoengineering as part of an overall strategy for meeting the 1.5°C Paris target
Abstract
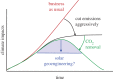
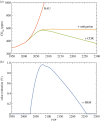
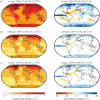
Solar geoengineering refers to deliberately reducing net radiative forcing by reflecting some sunlight back to space, in order to reduce anthropogenic climate changes; a possible such approach would be adding aerosols to the stratosphere. If future mitigation proves insufficient to limit the rise in global mean temperature to less than 1.5°C above preindustrial, it is plausible that some additional and limited deployment of solar geoengineering could reduce climate damages. That is, these approaches could eventually be considered as part of an overall strategy to manage the risks of climate change, combining emissions reduction, net-negative emissions technologies and solar geoengineering to meet climate goals. We first provide a physical-science review of current research, research trends and some of the key gaps in knowledge that would need to be addressed to support informed decisions. Next, since few climate model simulations have considered these limited-deployment scenarios, we synthesize prior results to assess the projected response if solar geoengineering were used to limit global mean temperature to 1.5°C above preindustrial in an overshoot scenario that would otherwise peak near 3°C. While there are some important differences, the resulting climate is closer in many respects to a climate where the 1.5°C target is achieved through mitigation alone than either is to the 3°C climate with no geoengineering. This holds for both regional temperature and precipitation changes; indeed, there are no regions where a majority of models project that this moderate level of geoengineering would produce a statistically significant shift in precipitation further away from preindustrial levels.This article is part of the theme issue 'The Paris Agreement: understanding the physical and social challenges for a warming world of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels'.
Keywords: 1.5; climate change; geoengineering.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- UNFCCC. 2015. Adoption of the Paris Agreement. See https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/2015/cop21/eng/l09.pdf.
-
- Rogelj J, Luderer G, Pietzcker RC, Kriegler E, Schaeffer M, Krey V, Riahi K. 2015. Energy system transformations for limiting end-of-century warming to below 1.5°C. Nat. Clim. Change 5, 519–527. ( 10.1038/nclimate2572) - DOI
-
- Sanderson B, O’Neill B, Tebaldi C. 2016. What would it take to achieve the Paris temperature targets? Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 7133–7142. ( 10.1002/2016GL069563) - DOI
-
- National Academy of Sciences. 2015. Climate intervention: carbon dioxide removal and reliable sequestration. Washington DC: The National Academies Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
