Types I and II Keratin Intermediate Filaments
- PMID: 29610398
- PMCID: PMC5880164
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018275
Types I and II Keratin Intermediate Filaments
Abstract
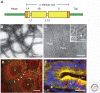
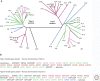
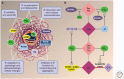
Keratins-types I and II-are the intermediate-filament-forming proteins expressed in epithelial cells. They are encoded by 54 evolutionarily conserved genes (28 type I, 26 type II) and regulated in a pairwise and tissue type-, differentiation-, and context-dependent manner. Here, we review how keratins serve multiple homeostatic and stress-triggered mechanical and nonmechanical functions, including maintenance of cellular integrity, regulation of cell growth and migration, and protection from apoptosis. These functions are tightly regulated by posttranslational modifications and keratin-associated proteins. Genetically determined alterations in keratin-coding sequences underlie highly penetrant and rare disorders whose pathophysiology reflects cell fragility or altered tissue homeostasis. Furthermore, keratin mutation or misregulation represents risk factors or genetic modifiers for several additional acute and chronic diseases.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Beil M, Micoulet A, von Wichert G, Paschke S, Walther P, Omary MB, Van Veldhoven PP, Gern U, Wolff-Hieber E, Eggermann J, et al. 2003. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine regulates keratin network architecture and visco-elastic properties of human cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol 5: 803–811. - PubMed
-
- Bouameur JE, Favre B, Borradori L. 2014. Plakins, a versatile family of cytolinkers: Roles in skin integrity and in human diseases. J Invest Dermatol 134: 885–894. - PubMed
-
- Chou CF, Omary MB. 1993. Mitotic arrest-associated enhancement of O-linked glycosylation and phosphorylation of human keratins 8 and 18. J Biol Chem 268: 4465–4472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
