Direct Detection of the Ion Pair to Free Ions Transformation upon Complexation with an Ion Receptor in Non-Polar Solvents by using Conductometry
- PMID: 29610717
- PMCID: PMC5878105
- DOI: 10.1002/open.201800014
Direct Detection of the Ion Pair to Free Ions Transformation upon Complexation with an Ion Receptor in Non-Polar Solvents by using Conductometry
Abstract
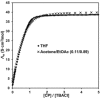
In this study, we performed conductometry in various organic solvents to directly detect the transformation from tetrabutylammonium chloride (TBACl) ion-pair salt to the free ions through complexation with meso-octamethylcalix[4]pyrrole (CP), which is a well-known receptor for chloride anions. In the presence of CP, the conductivity of TBACl increases in various non-polar solvents, indicating that complexation with CP enhances the ionic dissociation of TBACl in such non-polar solvents. In other words, CP recognizes chloride as an ion-paired salt as well as a free anion in non-polar solvents. Additionally, the TBA(CP-Cl) complex exhibited a considerably lower ion-pairing constant (Kip) than TBACl in non-polar solvents, resulting in enhanced conductivity. Based on these findings, we can conclude that complexation of an anion with a hydrophobic anion receptor will be useful for creating functional and stimuli-responsive soft materials in organic solvents using coulombic forces.
Keywords: anions; host–guest systems; molecular recognition; receptors; supramolecular chemistry.
Figures





References
-
- Lehn J.-M., Supramolecular Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1996.
-
- None
-
- de Silva A. P., Gunaratne H. Q. N., Gunnlaugsson T., Huxley A. J. M., McCoy C. P., Rademacher J. T., Rice T. E., Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1515–1566. - PubMed
-
- None
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

