Influence of Sodium Hyaluronate Concentration on Corneal Aberrations in Soft Contact Lens Wearers
- PMID: 29611370
- PMCID: PMC5906407
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2017.0099
Influence of Sodium Hyaluronate Concentration on Corneal Aberrations in Soft Contact Lens Wearers
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the influence of varying concentrations of sodium hyaluronate (SH) eye drops on corneal aberrations in normal individuals wearing silicone hydrogel contact lenses.
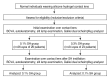
Methods: Normal individuals wearing silicone hydrogel contact lenses were enrolled in this study. Subjects were classified into two groups depending on the concentration of the preservative-free SH used (group 1, 0.1% SH; group 2, 0.3% SH). All subjects were asked to blink five times after instillation of the SH eye drop and before the Galilei measurements. Corneal aberrations were measured over the contact lenses before and after SH eye drop instillation. Visual acuity (VA) over the contact lenses was also measured both before instillation of the SH eye drop and after the subjects completed the five blinks.
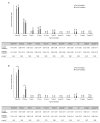
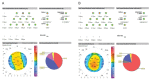
Results: There was no change in VA after SH instillation in group 1; however, group 2's VA significantly deteriorated after SH instillation. Changes in VA after SH instillation compared to baseline were significantly higher in group 2 than in group 1. Similarly, the increase in corneal aberrations after SH instillation was significant in group 2 but not significant in group 1. Among the significantly increased corneal aberration parameters, defocus was the main type in group 2. Changes in corneal aberrations after SH instillation compared to baseline were significantly higher in group 2 than in group 1.
Conclusions: A 0.3%-concentration of SH increases corneal aberration and decreases VA in soft contact lens wearers. Defocus is the main type of aberration that increased in the 0.3% SH instillation group.
Keywords: Contact lenses; Hyaluronic acid; Visual acuity; Wavefront aberration.
© 2018 The Korean Ophthalmological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of sodium hyaluronate on wavefront aberrations in dry eye patients.Optom Vis Sci. 2014 Jan;91(1):39-46. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000101. Optom Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24366433 Clinical Trial.
-
Optical quality and visual performance with customised soft contact lenses for keratoconus.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2014 Sep;34(5):528-39. doi: 10.1111/opo.12133. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2014. PMID: 24758229
-
Visual Performance and Optical Quality of Standardized Asymmetric Soft Contact Lenses in Patients With Keratoconus.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Jun 1;58(7):2899-2905. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-21296. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28586914
-
[Quantitative assessment of quality of vision].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):770-807; discussion 808. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656087 Review. Japanese.
-
Customised aberration-controlling corrections for keratoconic patients using contact lenses.Clin Exp Optom. 2020 Jan;103(1):31-43. doi: 10.1111/cxo.12937. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Clin Exp Optom. 2020. PMID: 31264266 Review.
Cited by
-
Corneal topography and angle parameters after laser iridotomy combined with iridoplasty assessed by dual Scheimpflug analyzer.Int Ophthalmol. 2020 Feb;40(2):447-457. doi: 10.1007/s10792-019-01205-6. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Int Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31720953
-
Sodium hyaluronate promotes proliferation, autophagy, and migration of corneal epithelial cells by downregulating miR-18a in the course of corneal epithelial injury.Eur J Histochem. 2023 Jun 15;67(2):3663. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2023.3663. Eur J Histochem. 2023. PMID: 37322995 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Outcome of Corneal and Anterior Chamber Angle Parameters after Combined Laser Iridotomy and Iridoplasty Using Dual Scheimpflug Analyzer: 1 Year Results.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 3;11(3):813. doi: 10.3390/jcm11030813. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35160264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glasson MJ, Stapleton F, Keay L, Willcox MD. The effect of short term contact lens wear on the tear film and ocular surface characteristics of tolerant and intolerant wearers. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2006;29:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Caffery BE, Richter D, Simpson T, et al. CANDEES: the Canadian Dry Eye Epidemiology Study. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;438:805–806. - PubMed
-
- Young G, Veys J, Pritchard N, Coleman S. A multi-centre study of lapsed contact lens wearers. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2002;22:516–527. - PubMed
-
- Dumbleton K, Woods C, Fonn D. An investigation of the efficacy of a novel ocular lubricant. Eye Contact Lens. 2009;35:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Begley CG, Caffery B, Nichols KK, Chalmers R. Responses of contact lens wearers to a dry eye survey. Optom Vis Sci. 2000;77:40–46. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources