Clinical Outcomes and Sustainability of Using CYP2C19 Genotype-Guided Antiplatelet Therapy After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- PMID: 29615454
- PMCID: PMC5889089
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.117.002069
Clinical Outcomes and Sustainability of Using CYP2C19 Genotype-Guided Antiplatelet Therapy After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Abstract
Background: CYP2C19 loss-of-function (LOF) alleles impair clopidogrel effectiveness after percutaneous coronary intervention. The feasibility, sustainability, and clinical impact of using CYP2C19 genotype-guided dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) selection in practice remains unclear.
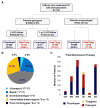
Methods: A single-center observational study was conducted in 1193 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention and received DAPT after implementation of an algorithm that recommends CYP2C19 testing in high-risk patients and alternative DAPT (prasugrel or ticagrelor) in LOF allele carriers. The frequency of genotype testing and alternative DAPT selection were the primary implementation end points. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular and clinically significant bleeding events over 12 months were compared across genotype and DAPT groups by proportional hazards regression.
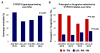
Results: CYP2C19 genotype was obtained in 868 (72.8%) patients. Alternative DAPT was prescribed in 186 (70.7%) LOF allele carriers. CYP2C19 testing (P<0.001) and alternative DAPT use in LOF allele carriers (P=0.001) varied over time. Risk for major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular was significantly higher in LOF carriers prescribed clopidogrel versus alternative DAPT (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.65; 95% confidence interval, 2.22-10.0; P<0.001), whereas no significant difference was observed in those without a LOF allele (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-2.85; P=0.347). Bleeding event rates were similar across groups (log-rank P=0.816).
Conclusions: Implementing CYP2C19 genotype-guided DAPT is feasible and sustainable in a real-world setting but challenging to maintain at a consistently high level of fidelity. The higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular associated with clopidogrel use in CYP2C19 LOF allele carriers suggests that use of genotype-guided DAPT in practice may improve clinical outcomes.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; clopidogrel; cytochrome P-450 CYP2C19; genetic testing; percutaneous coronary intervention; pharmacogenetics; precision medicine.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
Implementation of Genotype-Guided Antiplatelet Therapy: Feasible but Not Without Obstacles.Circ Genom Precis Med. 2018 Apr;11(4):e002118. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.118.002118. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2018. PMID: 29615455 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letter by Aw et al Regarding Article, "Clinical Outcomes and Sustainability of Using CYP2C19 Genotype-Guided Antiplatelet Therapy After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention".Circ Genom Precis Med. 2018 Jul;11(7):e002253. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.118.002253. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2018. PMID: 29987115 No abstract available.
-
Response by Lee and Stouffer to Letter Regarding Article, "Clinical Outcomes and Sustainability of Using CYP2C19 Genotype-Guided Antiplatelet Therapy After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention".Circ Genom Precis Med. 2018 Jul;11(7):e002258. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.118.002258. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2018. PMID: 29987116 No abstract available.
References
-
- Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, Bailey SR, Bittl JA, Cercek B, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. Circulation. 2011;124:e574–651. - PubMed
-
- Brilakis ES, Patel VG, Banerjee S. Medical management after coronary stent implantation: a review. JAMA. 2013;310:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Fan W, Plent S, Prats J, Deliargyris EN. Trends in P2Y12 inhibitor use in patients referred for invasive evaluation of coronary artery disease in contemporary US practice. Am J Cardiol. 2016;117:1439–1443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

