Biogeography of Leptospira in wild animal communities inhabiting the insular ecosystem of the western Indian Ocean islands and neighboring Africa
- PMID: 29615623
- PMCID: PMC5883017
- DOI: 10.1038/s41426-018-0059-4
Biogeography of Leptospira in wild animal communities inhabiting the insular ecosystem of the western Indian Ocean islands and neighboring Africa
Abstract
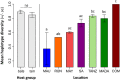
Understanding the processes driving parasite assemblages is particularly important in the context of zoonotic infectious diseases. Leptospirosis is a widespread zoonotic bacterial infection caused by pathogenic species of the genus Leptospira. Despite a wide range of animal hosts, information is still lacking on the factors shaping Leptospira diversity in wild animal communities, especially in regions, such as tropical insular ecosystems, with high host species richness and complex biogeographical patterns. Using a large dataset (34 mammal species) and a multilocus approach at a regional scale, we analyzed the role of both host species diversity and geography in Leptospira genetic diversity in terrestrial small mammals (rodents, tenrecs, and shrews) and bats from 10 different islands/countries in the western Indian Ocean (WIO) and neighboring Africa. At least four Leptospira spp. (L. interrogans, L. borgpetersenii, L. kirschneri, and L. mayottensis) and several yet-unidentified genetic clades contributed to a remarkable regional Leptospira diversity, which was generally related to the local occurrence of the host species rather than the geography. In addition, the genetic structure patterns varied between Leptospira spp., suggesting different evolutionary histories in the region, which might reflect both in situ diversification of native mammals (for L. borgpetersenii) and the more recent introduction of non-native host species (for L. interrogans). Our data also suggested that host shifts occurred between bats and rodents, but further investigations are needed to determine how host ecology may influence these events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Three Leptospira Strains From Western Indian Ocean Wildlife Show Highly Distinct Virulence Phenotypes Through Hamster Experimental Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 11;10:382. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00382. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30915044 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Tenrec ecaudatus, a Wild Mammal Introduced to Mayotte Island, as a Reservoir of the Newly Identified Human Pathogenic Leptospira mayottensis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Aug 30;10(8):e0004933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004933. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27574792 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of pathogenic leptospires from wild, domestic and captive host species in Portugal.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020 Mar;67(2):852-864. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13409. Epub 2019 Nov 24. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020. PMID: 31677243
-
Leptospirosis in the western Indian Ocean islands: what is known so far?Vet Res. 2013 Sep 9;44(1):80. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-80. Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 24016311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology of leptospirosis in Tanzania: A review of the current status, serogroup diversity and reservoirs.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Nov 16;15(11):e0009918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009918. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34784354 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Complete Genome Sequences of Three Leptospira mayottensis Strains from Tenrecs That Are Endemic in the Malagasy Region.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018 Oct 18;7(15):e01188-18. doi: 10.1128/MRA.01188-18. eCollection 2018 Oct. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018. PMID: 30533730 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Radiation of Leptospira and Tenrecidae (Afrotheria) on Madagascar.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 18;7(8):193. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7080193. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36006285 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Human Leptospirosis between Mayotte and Reunion Islands Highlights Distinct Clinical and Microbial Features Arising from Distinct Inter-Island Bacterial Ecology.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024 Jul 2;111(2):237-245. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0846. Print 2024 Aug 7. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024. PMID: 38955193 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. Infection in Cattle from Central and Northern Madagascar.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jun 6;16(11):2014. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16112014. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31174244 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral African Bats Brought Their Cargo of Pathogenic Leptospira to Madagascar under Cover of Colonization Events.Pathogens. 2023 Jun 21;12(7):859. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12070859. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37513706 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
